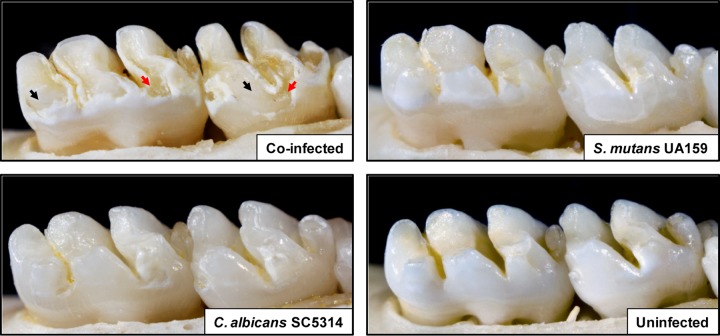
FIG 3.
Images of teeth from rats infected with S. mutans UA159 and/or C. albicans SC5314, or left uninfected, after 2 weeks. Photographs of lower molars in the rodent jaws are shown; jaws representing the average result have been selected. For the coinfected animal, black arrows indicate moderate to severe carious lesions where areas of the enamel are missing, exposing the underlying dentin. In some areas, the dentin is eroded or missing (red arrows), indicating the most severe carious lesions. In the S. mutans-infected animal, large areas of initial lesions were detected, although they were visibly less severe than those of coinfected animals. In the C. albicans-infected animal, small areas of demineralization and initial lesions were observed. In the uninfected animal, overt carious lesions are absent, while “white spots” (very early lesions) begin to appear in some localized areas.