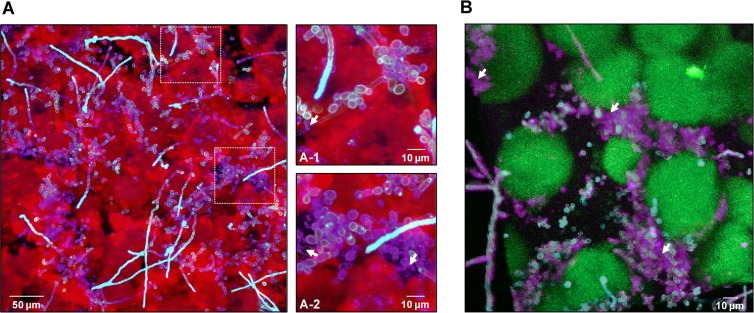
FIG 8.
Visualization and spatial distribution of β-glucan within cospecies biofilms. (A) Projection image of 42-h cospecies biofilms labeled with an anti-β-glucan antibody (purple), Alexa Fluor 647-dextran (EPS) (red), and ConA-tetramethylrhodamine (C. albicans cells) (blue). The image shows the presence of β-glucan (purple) within the biofilm, while the arrows in the closeup images of selected areas indicate punctate accumulations of β-glucan (A-1) that appear to be localized extracellularly (A-2). (B) Three-dimensional projection of a separate 42-h cospecies biofilm labeled with the anti-β-glucan antibody (purple), GFP (S. mutans cells) (green), and ConA-tetramethylrhodamine (C. albicans cells) (blue). The arrows indicate extracellular accumulations of β-glucan that appear to enmesh the C. albicans cells. Clearly, β-glucan can be found intercalated between C. albicans cells and S. mutans microcolonies, potentially having a structural role.