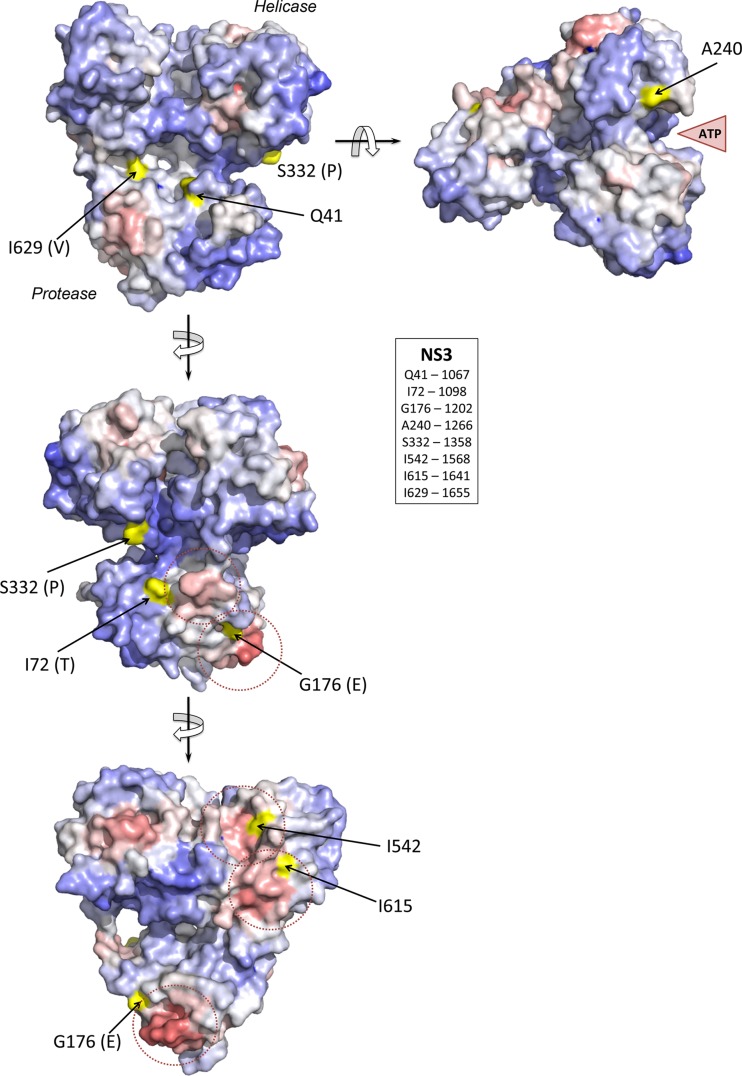
FIG 8.
Structural context of mutations occurring in the NS3 protein of H77S.2 virus during persistent infection of chimpanzee 4x0193, modeled on the structure of the bifunctional protease-helicase of genotype 1b BK strain of HCV (PDB entry 1CU1). Residues at which mutations were identified (Table 1) are labeled according to the H77S.2 sequence with the authentic BK residue shown in parentheses. Solvent-accessible surfaces of these residues are shaded in yellow, while the overall surface of the structure is colored according to ProMate output, with red shading representing high probability and blue shading a low probability that each surface residue contributes to a protein-protein interaction site (see Materials and Methods). Protein-protein interaction sites predicted by ProMate are shown encircled by a dashed red line. The single mutation identified in NS4A (R1691K, a reversion of a cell culture-adaptive mutation) occurs at residue 34 of NS4A and is located just outside the ordered structure of the NS4A peptide strand in the NS3/4A complex.