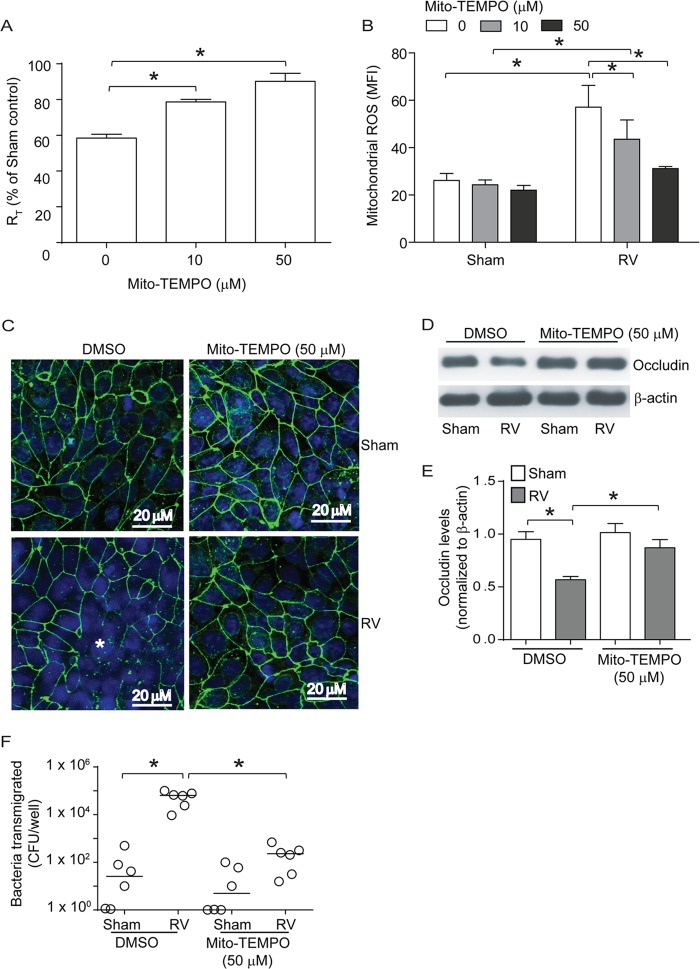
FIG 4.
Mito-Tempo, an antioxidant targeted to mitochondria, blocks RV-induced reduction in RT and mitochondrial ROS generation. Polarized monolayers of 16HBE14o− cells were treated with 0, 10, or 50 μM Mito-Tempo for 1 h both apically and basolaterally. (A and B) Cells were infected with RV or sham control apically and incubated for 90 min. The infection medium was replaced with fresh medium containing 0, 10, or 50 μM Mito-Tempo and incubated for an additional 24 h. The RT was measured, and then the cells were washed and incubated with MitoSox Red as described for Fig. 3 and analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Polarized cells were infected with RV or sham control in the presence of 0 or 50 μM Mito-Tempo and incubated for 24 h. The cells were fixed, blocked with 1% BSA in PBS, and incubated with antibody to occludin. Bound antibody was detected with antirabbit IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488, and the cells were counterstained with DAPI and then subjected to indirect immunofluorescence microscopy. The images are representative of 3 or 4 independent experiments (*, dissociation of occludin from the tight-junction complex; green, occludin; blue, nuclei). (D and E) NP-40-insoluble fractions from cells infected with RV or sham control in the presence or absence of Mito-Tempo were subjected to Western blot analysis, and the band intensities were quantified using NIH Image J and expressed as fold change over β-actin. (F) Serial dilutions of basolateral media from cell cultures infected with RV or sham control in the presence or absence of Mito-Tempo were plated to determine the number of bacteria transmigrated from the apical to the basolateral surface. The data in panels A, B, and D represent means and SD calculated from 3 or 4 independent experiments (*, P ≤ 0.05; ANOVA). The data in panel F represent medians with ranges from 3 independent experiments (*, P ≤ 0.05; ANOVA on ranks).