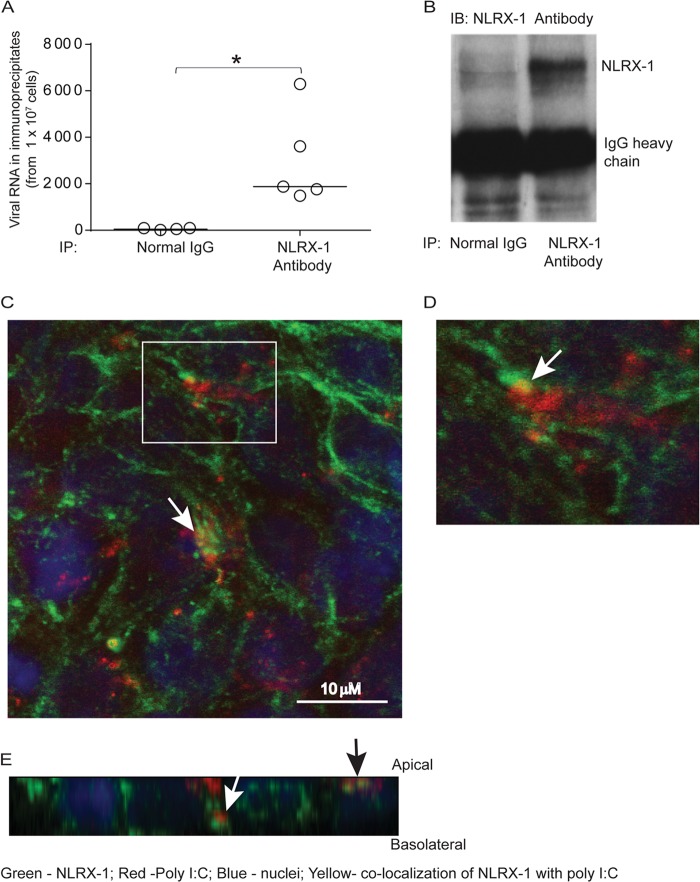
FIG 7.
NLRX-1 interacts with viral RNA and poly(I·C). The polarized airway epithelial cells were RV or sham infected and incubated for 16 h, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with normal IgG or anti-NLRX-1 antibody. (A and B) Total RNA was isolated from the immunoprecipitates, the RV RNA copy number was determined (A), and an aliquot of immunoprecipitates (IP) was subjected to Western blot (IB) analysis with NLRX-1 antibody (B). (C to E) Rhodamine-labeled poly(I·C) was added to the apical surfaces of polarized airway epithelial cells and incubated for 3 h. The cells were fixed in methanol, blocked with BSA, incubated with antibody to NLRX-1 conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488, and counterstained with DAPI. The cells were visualized by confocal microscopy. Panel D is a magnified view of the boxed area in panel C. Panel E shows a Z section of panel C. The white arrows in panels C and D indicate colocalization of poly(I·C) with NLRX-1. The white and black arrows in panel E represent NLRX-1 colocalization with poly(I·C) in the subapical and apical locations, respectively. The data in panel A represent medians and ranges from 5 independent experiments (*, P ≤ 0.05; ANOVA). The images are representative of three or five independent experiments.