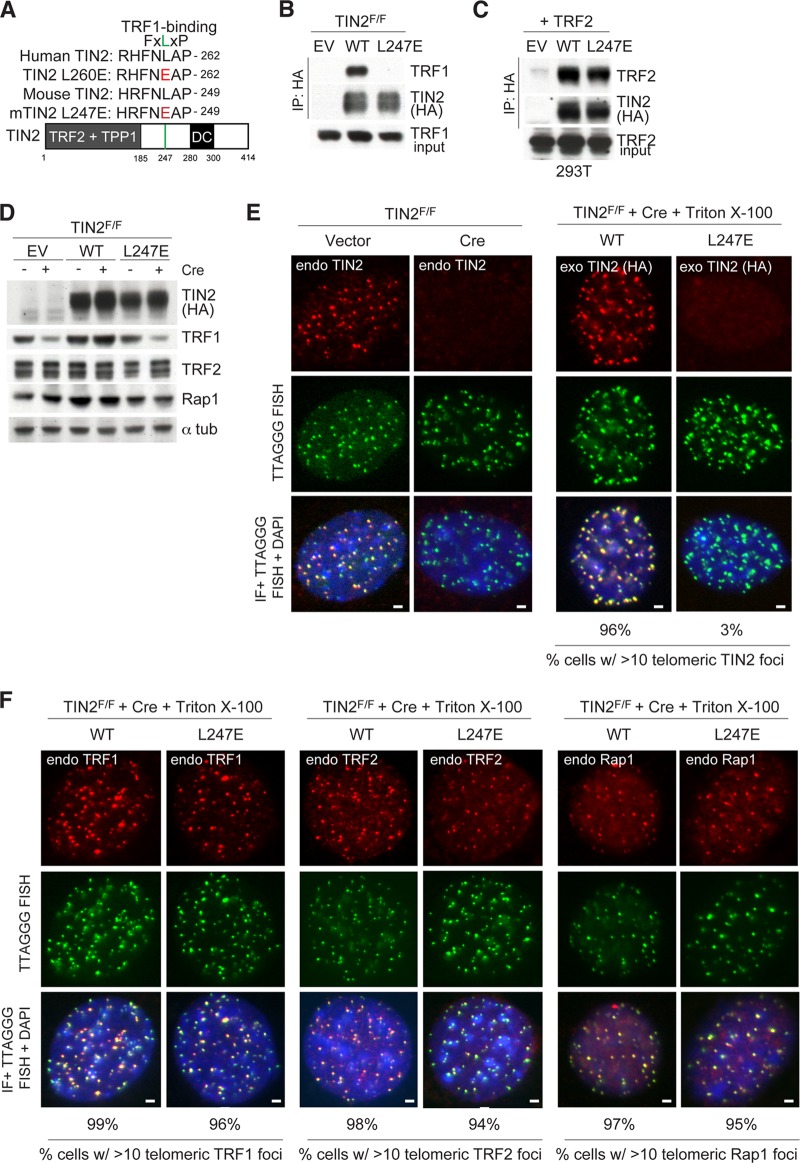
FIG 1.
TIN2 allele lacking TRF1 binding is lost at telomeres. (A) Schematic of the mouse TIN2 protein indicating regions of shelterin binding and location of mutations identified in dyskeratosis congenita (DC) patients. Homology between human and mouse TIN2 is shown surrounding the FXLXP TRF1 binding motif. Amino acids in red indicate mutations introduced to generate TRF1 binding mutants. (B) Cell extracts from TIN2F/F MEFs exogenously expressing the indicated FLAG-HA2 TIN2 alleles were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-HA resin, and immunocomplexes were probed for the indicated proteins. (C) Cell extracts from 293T cells coexpressing the indicated FLAG-HA2 TIN2 alleles and TRF2 were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA resin, and immunocomplexes were probed for the indicated proteins. (D) Immunoblotting of cell extracts from TIN2F/F MEFs expressing TIN2 alleles (as in panel B) or empty vector (EV) with or without Cre treatment (72 h). (E) Left, loss of TIN2 as observed by IF-FISH from TIN2F/F MEFs with or without Cre treatment (72 h). Right, IF of FLAG-HA2 TIN2 alleles (anti-HA antibody, red) and telomeric FISH (green) following Triton X-100 extraction of soluble proteins in TIN2−/− MEFs (72 h post-Cre). (F) Left, IF of TRF2 (anti-TRF1 antibody, red) in cells expressing FLAG-HA2 TIN2 alleles and telomeric FISH (green) following Triton X-100 extraction of soluble proteins in TIN2−/− MEFs (72 h post-Cre). Middle, IF of TRF2 (anti-TRF2 antibody, red) in cells expressing FLAG-HA2 TIN2 alleles and telomeric FISH (green) following Triton X-100 extraction of soluble proteins in TIN2−/− MEFs (72 h post-Cre). Right, IF of Rap1 (anti-Rap1 antibody, red) in cells expressing FLAG-HA2 TIN2 alleles and telomeric FISH (green) following Triton X-100 extraction of soluble proteins in TIN2−/− MEFs (72 h post-Cre). DNA is stained with DAPI (blue). At least 200 cells were used for quantification of TIN2 and Rap1 foci. Bars, 1.5 μm.