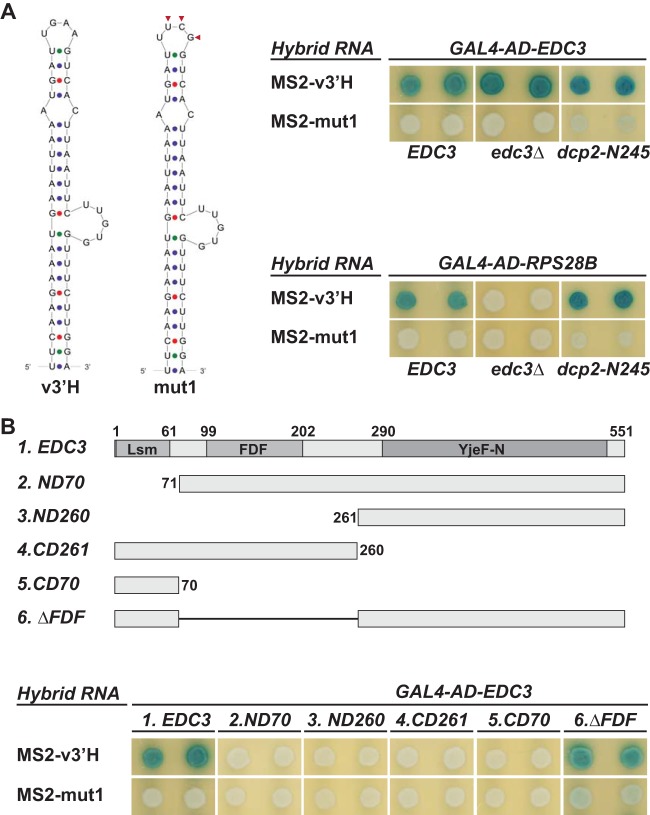
FIG 6.
Edc3, but not Rps28b, binds directly to the RPS28B 3′ UTR regulatory element. (A) Analysis of the binding of Edc3 and Rps28b to the RPS28B 3′ UTR element using the three-hybrid assay in a wild-type tester strain (YBZ1) and tester strains harboring an edc3Δ (SYY2691) or dcp2-N245 (SYY2693) allele. The primary sequences and secondary structures of the wild-type and mutant RPS28B 3′ UTR elements used in these analyses are shown on the left. Mutated nucleotides are indicated by red triangles. (B) Analysis of the binding of different Edc3 fragments to the RPS28B 3′ UTR element using the three-hybrid assay in the wild-type tester strain YBZ1. A schematic representation of Edc3 domain structure and edc3 fragments used in the analysis is shown at the top. In both panels A and B, DNA fragments encoding the wild-type (v3′H) and mutant (mut1) RPS28B 3′ UTR elements were fused to MS2 binding sites. The resulting hybrid RNAs were used for testing the interaction with full-length Edc3 or Rpd28b (A) and different fragments of Edc3 (B) fused to GAL4(AD) in the yeast three-hybrid system. In each case, a hybrid RNA and a GAL4(AD) fusion were cotransformed into the indicated tester strains. Individual transformants were selected, and qualitative β-galactosidase activity was determined on X-Gal-containing plates. Blue colony color indicates an interaction, and white colony color indicates no interaction.