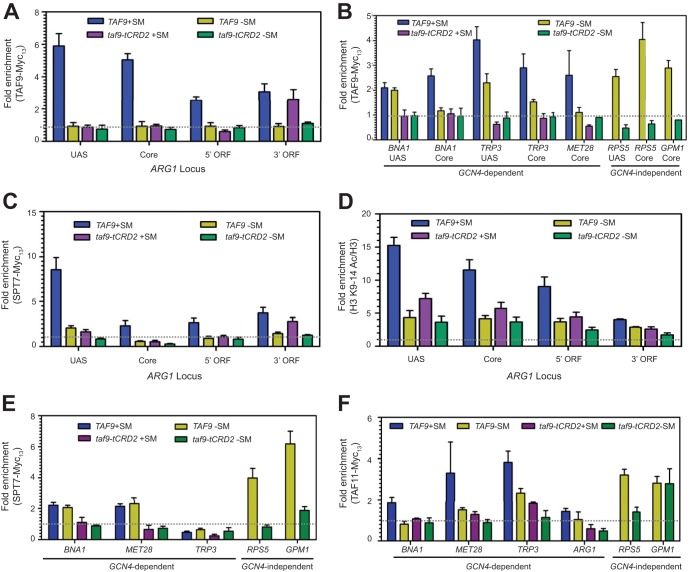
FIG 6.
The Taf9 CRD is required for occupancy of Taf9 complexes in vivo. (A and B) Occupancy of Myc13-tagged Taf9 and Taf9-tCRD2 at the ARG1 locus under SM-treated and untreated conditions (A) and occupancy at other Gcn4-dependent promoters under SM-treated and untreated conditions or at Gcn4-independent promoters RPS5 and GPM1 under non-SM-treated conditions (B). (C) Occupancy of Spt7-Myc13 at the ARG1 locus in TAF9 and taf9-tCRD2 strains under SM-treated and untreated conditions. (D) Levels of histone H3 K9/14Ac at the ARG1 locus under SM-treated and untreated conditions. A ChIP assay was done with anti-H3 K9/14Ac antibody and normalized to the total histone H3 level by immunoprecipitation with pan-anti-H3 antibody. (E) Spt7-Myc13 occupancy in TAF9 and taf9-tCRD2 strains in the UAS regions of the Gcn4-dependent promoters under SM-treated and untreated conditions or in the RPS5UAS and upstream region of GPM1 under non-SM-treated conditions. (F) Core promoter occupancy of Taf11-Myc13 at Gcn4-dependent targets in TAF9 and taf9-tCRD2 strains under SM-treated and untreated conditions or at RPS5 and GPM1 under non-SM-treated conditions. The POL1 coding sequence was used as a nonspecific control, except in panel D, where the TEL06R-XC region was used. For each analysis, enrichment values were obtained from 3 or 4 chromatin immunoprecipitation assays from at least two independent chromatin preparations. The error bars indicate SEM.