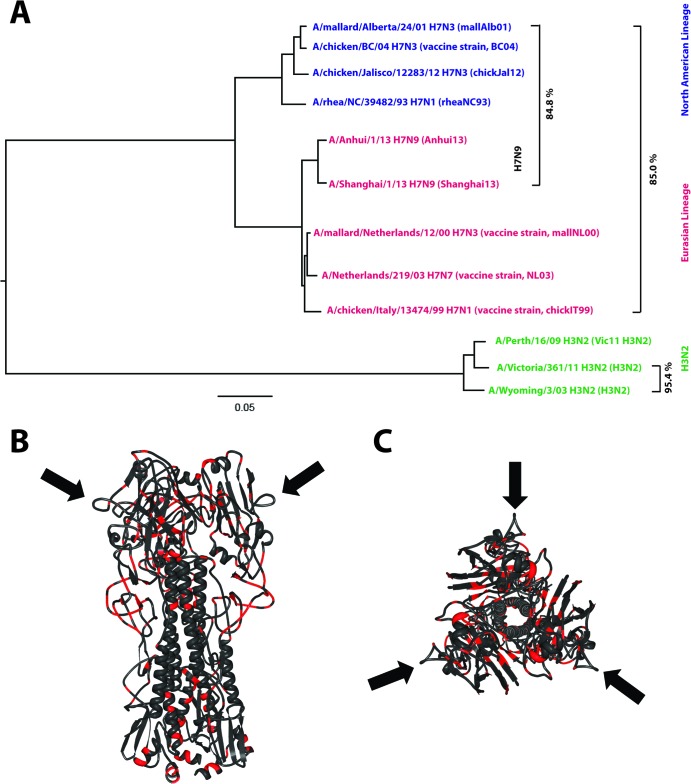
FIG 1.
Phylogenetic and antigenic relationship among H3 and H7 strains. (A) Phylogenetic tree based on HA sequences of North American (blue) and Eurasian (red) lineage H7 strains used in this study or in human clinical trials. H7N9 prototype strains are indicated. Drift in closely related H3N2 strains (95.4% amino acid identity between 2003 and 2009 isolates) mediates escape from HI-active antibodies quickly. HI cross-reactivity between distantly related H7 strains (e.g., mallAlb01 and Shanghai13 share only 84.8% amino acid identity) is probably mediated by conserved antigenic sites. The tree was built by using ClustalW and was visualized by using FigTree software. (B and C) Front view (B) and top view (C) of the HA trimer of A/Shanghai/2/13 (PDB accession number 4N5J [11]). Regions conserved among the vaccine strains tested in this study (Eurasian and North American lineages) are shown in dark gray, while nonconserved regions are shown in red. The completely conserved antigenic site A is indicated by black arrows.