FIG 2.
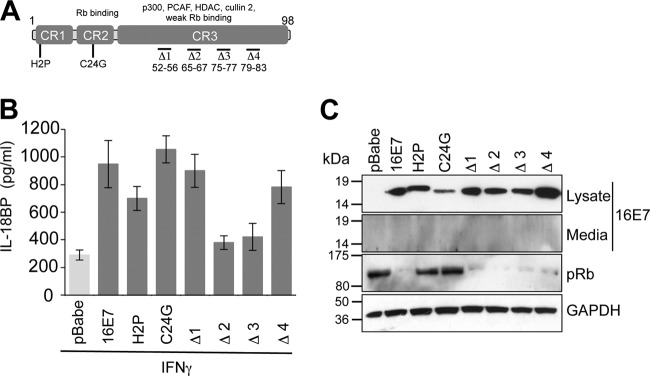
Enhanced IL-18BP expression requires amino acids in the carboxyl terminus of E7. (A) Schematic of E7 and the mutations used in this study. Functional regions of E7 are highlighted. Substitutions are shown, and small deletions are indicated by “Δ”. (B) Amino acids in CR3 are necessary for increased IL-18BP production. Primary human foreskin keratinocytes stably expressing empty plasmid (pBabe), 16E7, 16E7 H2P, 16E7 C24G, and four carboxyl-terminal truncations designated Δ1 (with deletion of amino acids 52 to 56), Δ2 (with deletion of amino acids 65 to 67), Δ3 (with deletion of amino acids 75 to 77), and Δ4 (with deletion of amino acids 79 to 83) were treated with IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 16 h. Following treatment, supernatants were harvested and levels of secreted IL-18BP measured by ELISA. Results are expressed as the means ± SD from four independent experiments. (C) Media and cell lysates from representative experiments were subjected to SDS-PAGE and probed with the indicated antibodies to confirm E7 expression and test functionality of the mutations. GAPDH was used to demonstrate equal loading of lysates.
