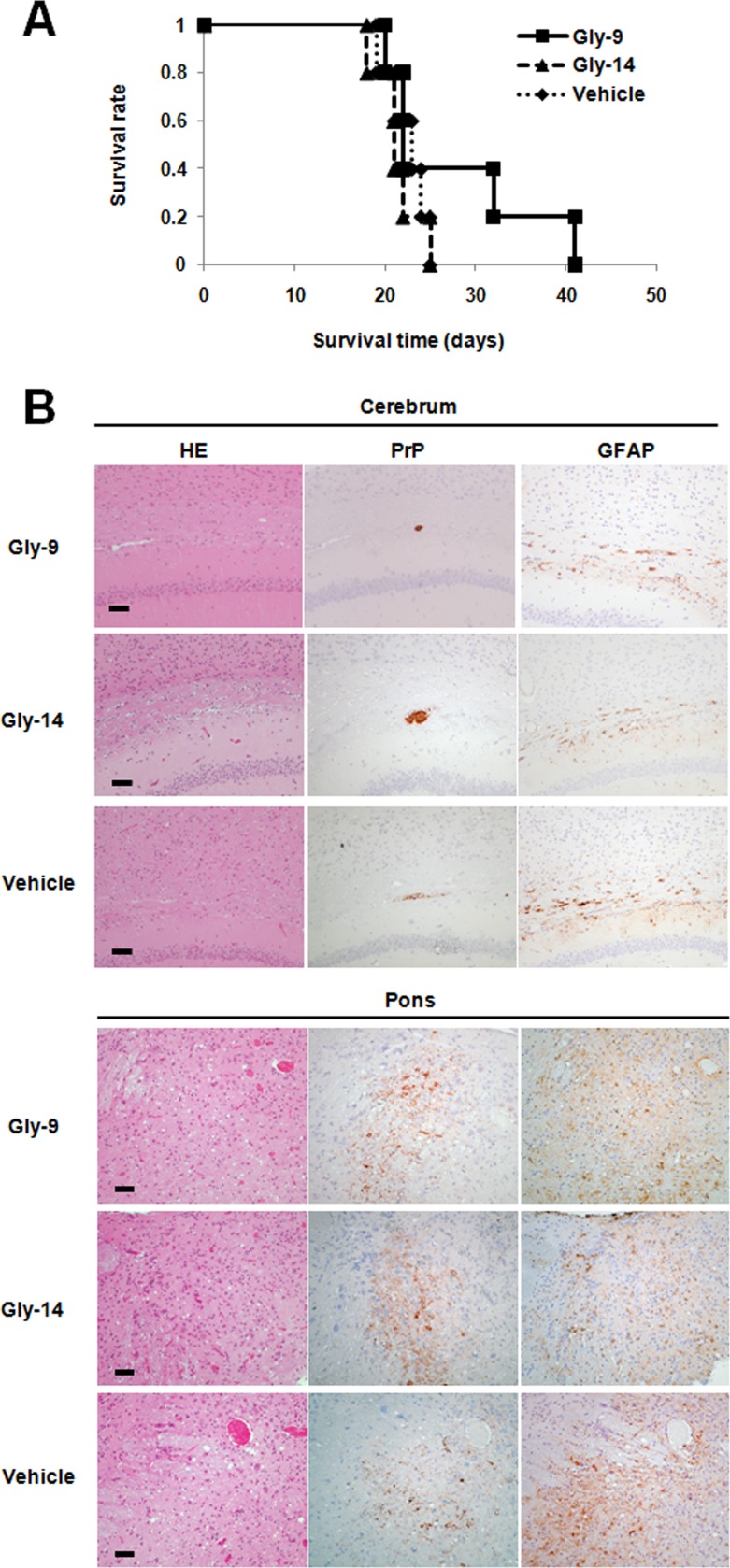
FIG 9.
Gly-9 effects on prion-infected animals. (A) Kaplan-Meier graph for animals treated with Gly-9. Tg7 mice infected intracerebrally with 263K prion were given intracerebroventricular injections of Gly-9 or Gly-14 at a dose of 300 μg/day or of vehicle continually from 6 weeks postinfection. The survival time in this study indicates the length of time from the start of injections to the onset of terminal disease. (B) Neuropathology of Gly-9-treated, terminally ill animals. Representative images stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) or immunolabeled for abnormal PrP deposition (PrP) or glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) are shown for the brain sections of animals treated as described for panel A. The images include the deep cerebral cortex, white matter, and hippocampus pyramidal cell layer (cerebrum) or the pontine laterodorsal tegmental area (Pons). Bars, 50 μm. It is noteworthy that the cerebral sections show coarse plaque-like PrP deposition and mild glial reactions in the white matter, whereas the pontine sections show moderate spongiosis, remarkable fine granular PrP deposition, and marked glial reactions. It is also noteworthy that no apparent difference in these neuropathological features exists among the three groups.