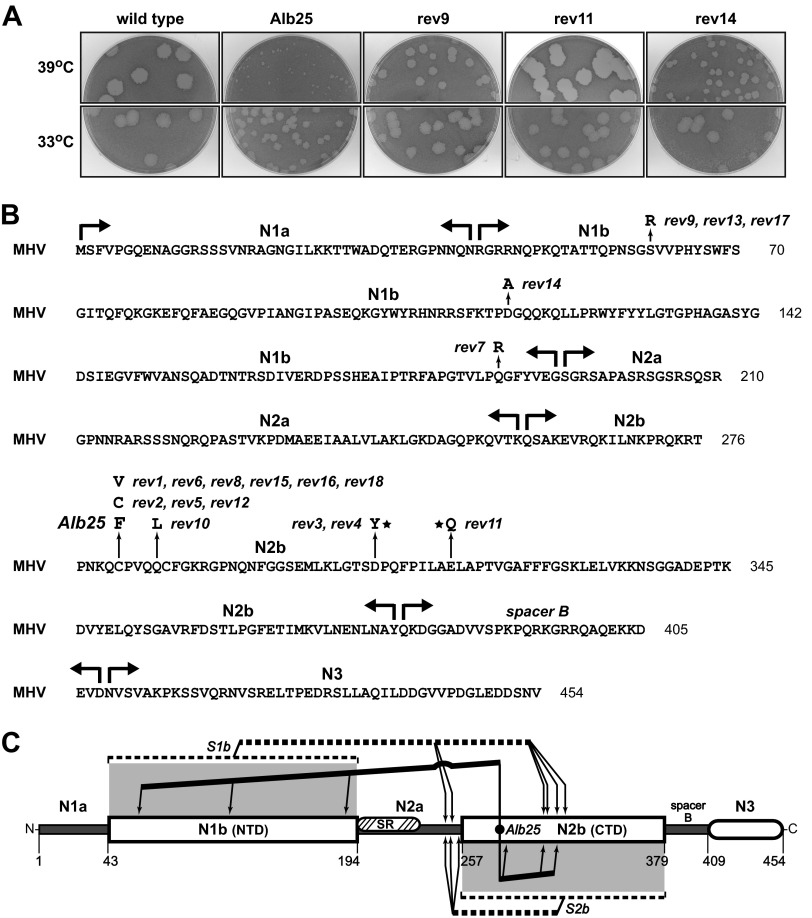
FIG 4.
Classical temperature-sensitive MHV N protein mutant Alb25 (39) and its revertants. (A) Plaques of representative examples of second-site Alb25 revertants at 33 or 39°C compared with those of the original Alb25 mutant and wild-type virus Alb240 (73). Plaque titrations were carried out on L2 cells; monolayers were stained with neutral red at 72 h postinfection and were photographed 18 h later. (B) MHV N protein amino acid sequence, showing domain boundaries and loci of the Alb25 mutation and 18 independent reverting mutations that partially or completely restore growth at the nonpermissive temperature. Stars denote reverting mutations at residues that were also mutated in particular S1b revertants. (C) Summary of N protein intramolecular genetic interactions revealed by revertants of the S1b, S2b, and Alb25 mutants. Lines running from the sites of the S1b or S2b substitutions or the Alb25 mutation point to the locations of compensating mutations.