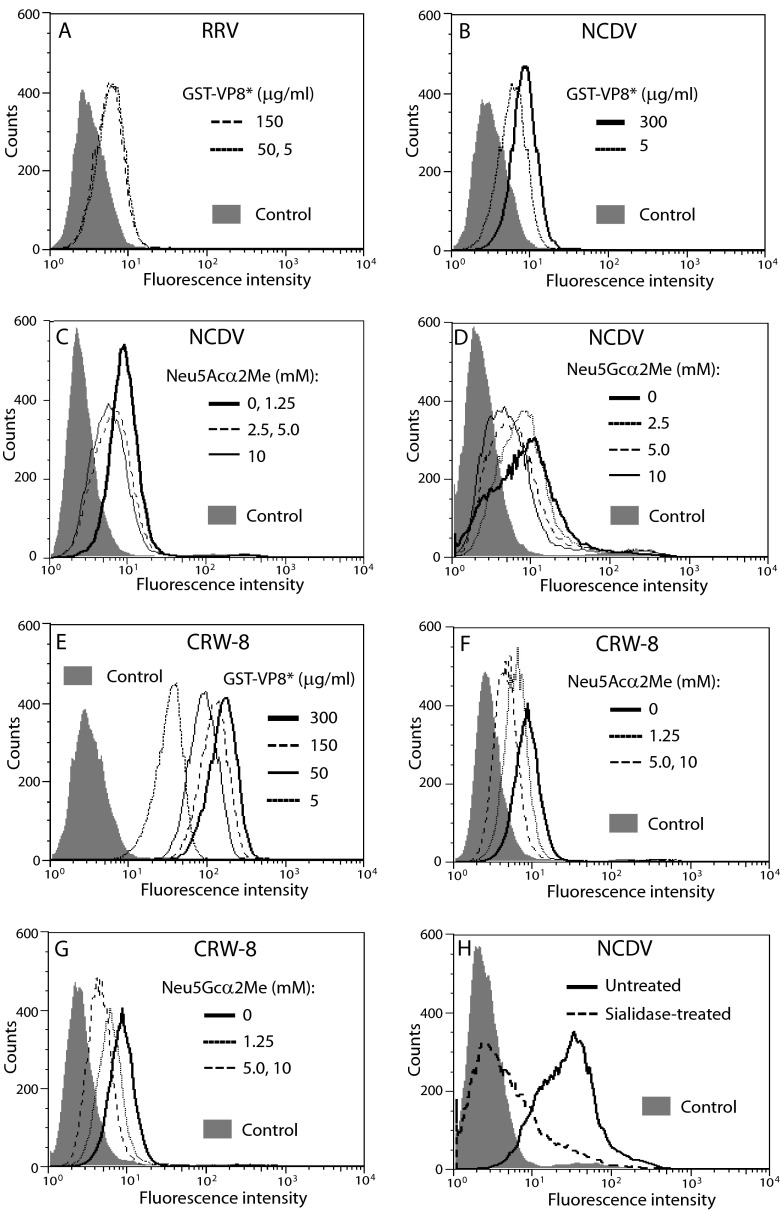
FIG 5.
Studies of Sia competition and sialidase sensitivity of cell binding by animal rotavirus VP8*. Cell binding by recombinant VP8* of RRV (A) and NCDV (B) at concentrations (μg/ml) of 5, 50, and 150 to cells placed into suspension using trypsin-EDTA treatment. NCDV GST-VP8* also was tested at 300 μg/ml. The histograms for NCDV VP8* at 150 μg/ml and 50 μg/ml fell close to and between those for 300 μg/ml and 5 μg/ml and are not shown for the sake of clarity. Cell binding by NCDV VP8* at 600 μg/ml (C and D) and CRW-8 VP8* at concentrations (μg/ml) of 5, 50, 150 and 300 (E) also are illustrated. Reduced cell binding by NCDV VP8* (C and D) at 600 μg/ml and CRW-8 VP8* at 5 μg/ml (F and G) following Neu5Acα2Me (C and F) and Neu5Gcα2Me (D and G) treatment is shown. (H) Cellular sialidase treatment reduced binding by NCDV VP8* (600 μg/ml). Reductions in GST-VP8* binding in panels C to G were analyzed for Neu5Acα2Me and Neu5Gcα2Me at concentrations (mM) of 1.25, 2.5, 5.0, and 10. Histograms for NCDV VP8* treated with 1.25 mM Neu5Gcα2Me were indistinguishable from those for untreated NCDV. Data for CRW-8 VP8* incubated with 2.5 mM Neu5Acα2Me or 2.5 mM Neu5Gcα2Me were indistinguishable from those of CRW-8 reacted with the respective Sia at 1.25 mM.