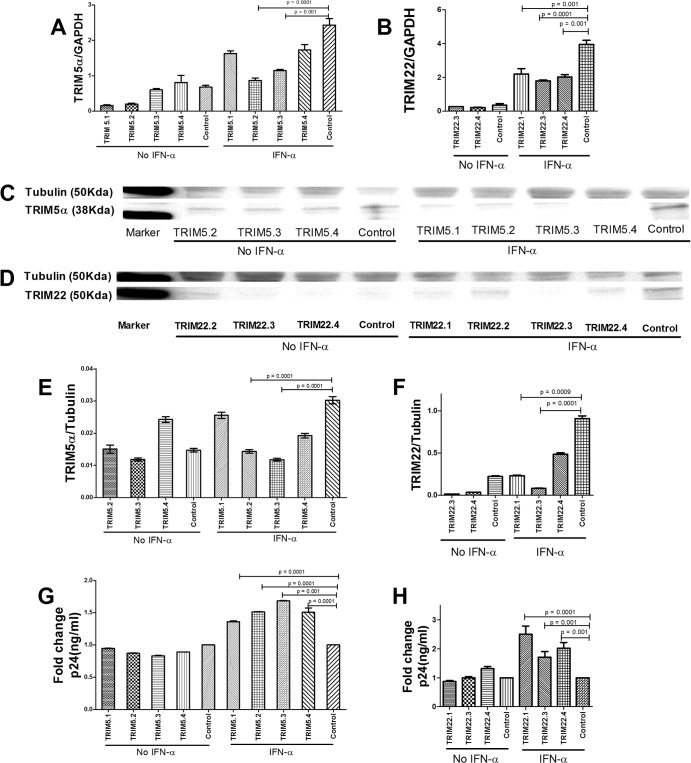
FIG 5.
siRNA-mediated silencing of TRIM5α or TRIM22 in CD4 cells. To determine the functional impact of TRIM5α and TRIM22 on HIV-1 replication in CD4 cells, gene knockdown experiments were performed by transducing the cells with siRNA against TRIM5α or TRIM22 or a nontargeting (scramble) control siRNA, with or without IFN-α stimulation for 24 h. (A to F) Knockdown of TRIM5α or TRIM22 by siRNA in the absence or presence of IFN-α was validated by mRNA RT-PCR (A and B) and Western blotting (C to F). Cells were then challenged with a VSV-G-pseudotyped HIV-1 laboratory strain (JRCSF) (600 ng of p24/ml) for 48 h. (G and H) Culture lysates were collected and assessed for HIV p24 antigen levels by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data are depicted as fold changes, where the levels of p24 antigen in knockdown cells were divided by the levels in control cells. TRIM22.2 siRNA knockdown efficiency was inconsistent, and the data are thus excluded from the graphs.