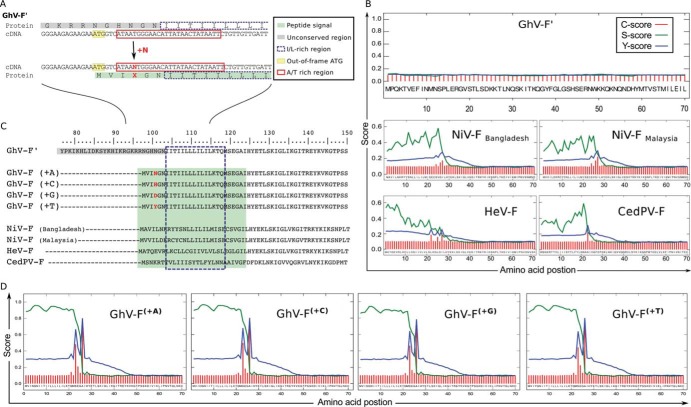
FIG 3.
A sequence correction in the N terminus of GhV-F′ creates a conserved signal peptide sequence. (A) Addition of one nucleotide in GhV-F′ creates a new start codon. Analysis of the protein and cDNA sequence in the unconserved region of GhV-F′ revealed an out-of-frame ATG (yellow box) close to an AT-rich region (red box). Insertion of one nucleotide (+N) at the indicated position (right after nucleotide 7,166 in the HQ660129.1 reference sequence) shifts the reading frame of F′, creates a new start codon from the upstream ATG (now position +1), and generates an amino acid insertion at position +4 (red X). (B) Signal peptide prediction for GhV-F′ and other HNV-F proteins. The first 70 amino acids of the indicated HNV-F proteins were bioinformatically analyzed for the presence of signal peptide sequences using four independent signal peptide prediction programs (Table 1). Results from the SignalP program are graphically presented, as described by Petersen et al. (13). SignalP is a neural network trained to predict signal peptides and provides three output scores for any query input sequence: the C score (raw cleavage site score [red]), S score (signal peptide score [green]), and Y score (combined cleavage site score [blue]). The C, S, and Y scores (y axis) for each amino acid (x axis) in the HNV-F query sequence are shown. In essence, the S score is high when the SignalP networks predict the sequence to be part of the signal peptide, while the C score is trained to recognize the SP cleavage site and is therefore highest at the first residue after the cleavage site. The Y score is a weighted score that helps identify the most likely cleavage site(s) when there are multiple C-score peaks. See http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/output.php for details. (C) Alignment of HNV-F amino acid sequences. Insertion of a single nucleotide in GhV-F′ creates an isoleucine-/leucine-rich N terminus (dashed box) with a conserved signal peptide (green box). (D) Signal peptide prediction for the rectified GhV-F(+1) proteins GhV-F(+A), GhV-F(+C), GhV-F(+G), and GhV-F(+T). Signal peptide motifs were analyzed using SignalP software, as described for panel B.