FIG 6.
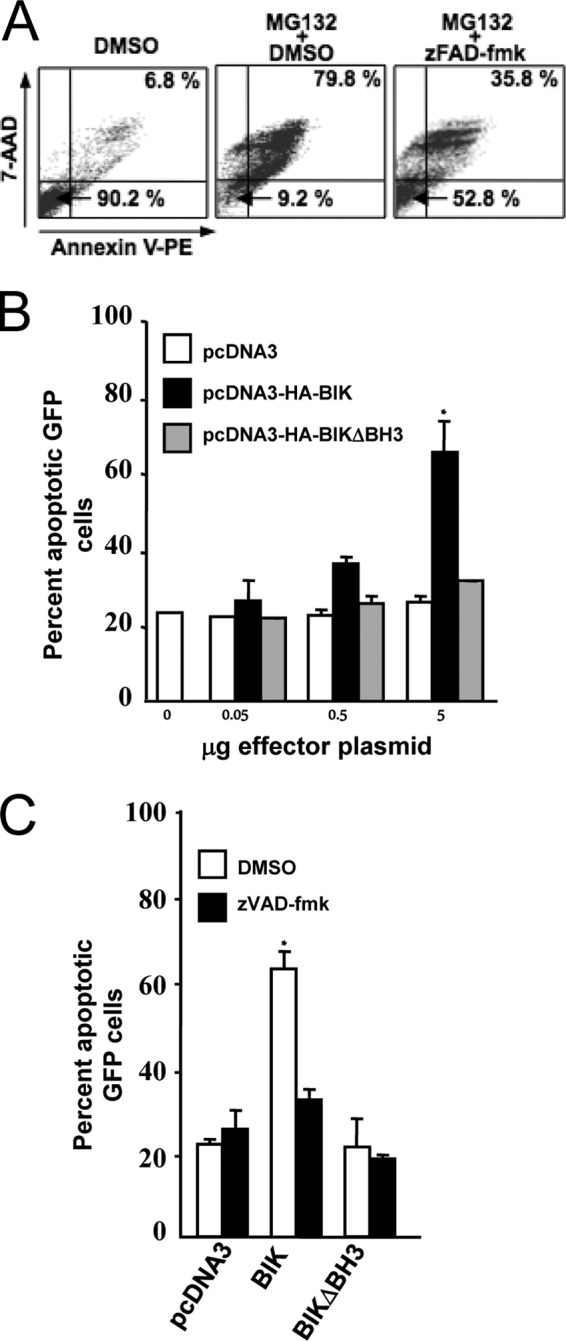
Ectopic BIK induces apoptosis in the LCL IB4 by a mechanism dependent on its BH3 domain and the activation of caspases. (A) Representative IB4 cell viability FACS profiles. IB4 cells were treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; vehicle) or the apoptosis-inducing proteasome inhibitor MG132 (15 mM) alone or in combination with the pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD-fmk (50 mM) or vehicle (DMSO). Twelve hours later, cells were then double-stained with Annexin V/7-AAD, and survival profiles were monitored by FACS. Viable cells (Annexin V− and 7-AAD−) and late-stage apoptotic cells (Annexin V+ and 7-AAD+) are represented in the bottom left and top right quadrants, respectively. Data for 10,000 cells were collected in each case, and the percentages of the total population in these quadrants are shown. (B) Dose-dependent induction of apoptosis by ectopic BIK in IB4. IB4 cells were cotransfected with 2 μg of pMaxGFP together with pcDNA3, pCDNA3-HABIK, or pcDNA3-HABIKDBH3 (quantities of effector plasmids used are indicated underneath). In all cases, the total amount of DNA used was kept constant at 7 μg by adding an appropriate amount of pcDNA3. Six hours later, cells were washed twice with PBS, and the survival profiles of GFP-expressing populations were determined as for panel A following 7-AAD/Annexin V staining. Data are means ± standard deviations. *, P < 0.05. The results shown were compiled from three separate transfections. (C) BIK-induced apoptosis is inhibited by the pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk. IB4 cells were transiently cotransfected as described for panel B and then immediately either treated or untreated with of 50 mM zVAD-fmk. Cell viability was analyzed 3 h later by 7-AAD/Annexin V staining as described for panel A. The percentage of GFP-expressing cells in late apoptosis was then plotted. Data are means ± standard deviations. *, P < 0.05. The results shown were generated from three separate transfections.
