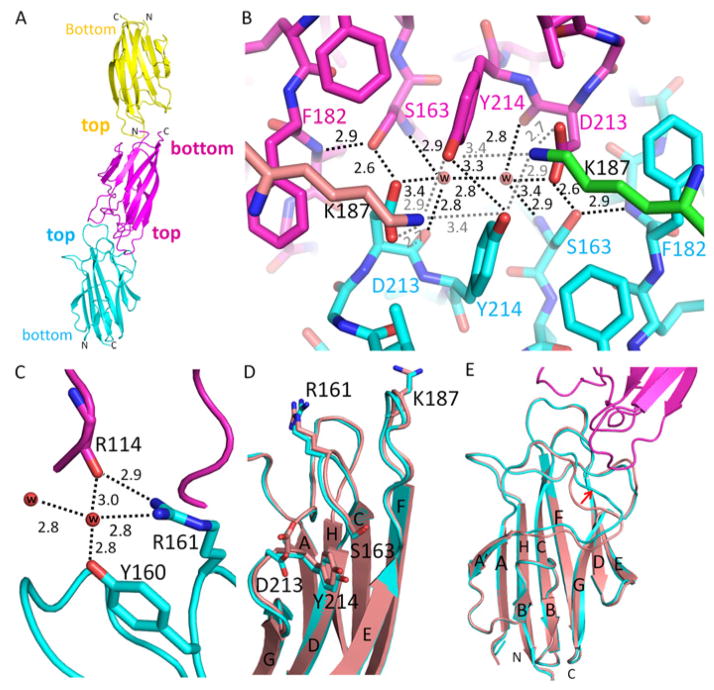
Fig. 2.
Intermolecular interactions of CIQTNF5 globular heads. (A) Colored yellow, magenta and cyan, three gC1q molecules in the asymmetric unit of space group P63 are stacked on each other in two ways: top-to-bottom and top-to-top. (B) An intermolecular hydrogen bond network facilitates top-to-top packing of two adjacent gC1q molecules. This intermolecular hydrogen bond network involves the pathogenic mutation residue S163, D213, two water molecules and Y214. This intermolecular hydrogen bond network is further extended to other molecules by K187. The two K187 residues are not from these two top-to-top packed gC1q molecules but rather from their respective trimerization partners, so their carbon atoms are colored in green and tint, respectively. Water molecules are represented with red balls. Hydrogen-bonds are shown with black or gray dotted lines. Distances are given in Å. (C) Water molecules connect R114 of one gC1q molecule with Y160 and R161 of another gC1q molecule by hydrogen bonds. (D) Structural comparison of gC1q domains involved (cyan) and uninvolved (tint, PDB: 4F3J) in top-to-top packing. Side chains of D213 and R161 are flipped in top-to-top packing. Y214 shows a slight conformational shift but S163 retains a nearly identical conformation. (E) Top-to-top intermolecular interaction features a conformational shift of the β-sheet A|A′ loop indicated by the red arrow. Structures of gC1q domains involved in top-to-top packing are colored cyan and magenta. The gC1q domain structure uninvolved in this type of packing is colored with tint (PDB: 4F3J).