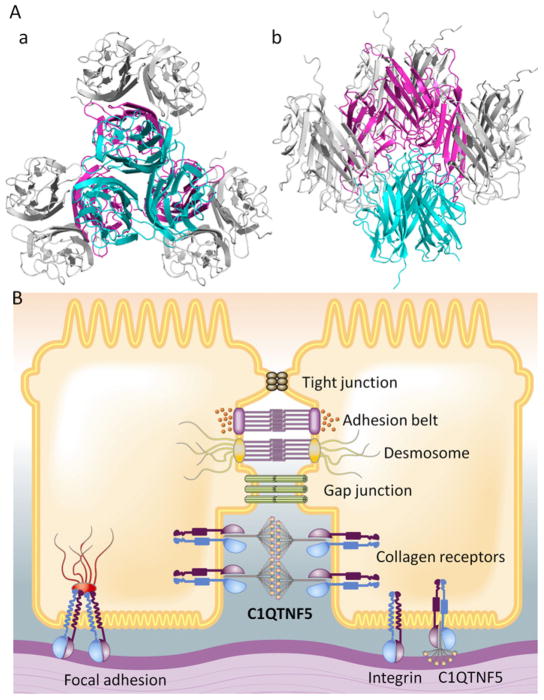
Fig. 3.
C1QTNF5 functions in RPE cellular adhesion through its globular heads. (A) Head-to-head interactions of C1QTNF5 present in space group P63: perpendicular view (a) and side view (b). Globular heads were generated by applying crystallographic 3-fold axes to the top-to-top interacting partner. Three gC1q monomers of one globular head respectively interact with other three globular heads. These interwoven interactions can assemble all neighboring C1QTNF5 multimers on adjacent RPE cell membranes together. (B) Globular heads of two bouquet-like C1QTNF5 multimers can interact with each other, whereas their collagen domains bind to collagen receptors on membranes of two adjacent RPE cells, thus filling the sub-retinal space and gluing the two RPE cells together.