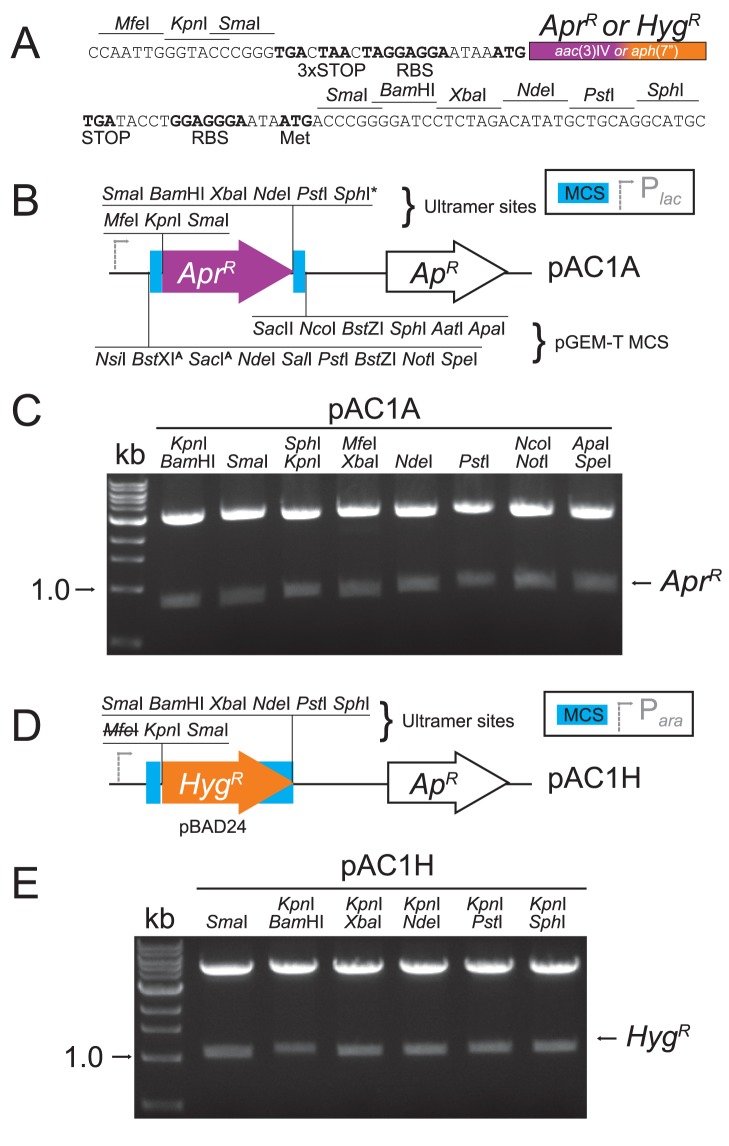
Figure 1. Synthesis of plasmids containing aph(7″) or aac(3)IV as non-polar hygromycin B and apramycin resistance markers.
(A) Schematic of ultramers designed to amplify aph(7″) or aac(3)IV. The 5′ ultramers 5631 and 5633, for aph(7″) or aac(3)IV respectively, include MfeI, KpnI and SmaI restriction sites, stop codons in all three reading frames, and a ribosome binding site. The 3′ ultramers 5632 and 5634 include a ribosome binding site, a start codon in-frame with restriction sites for SmaI and BamHI, and restriction sites for XbaI, NdeI, PstI and SphI. (B) The amplified aac(3)IV was introduced by TA cloning into linearized pGEM-T, conserving the restriction sites in the pGEM-T multiple cloning site (MCS). The resulting plasmid is pAC1A. The pGEM sites may also be used for the sub-cloning of the apramycin resistance marker (AprR). MCS sites that cut aac(3)IV are indicated with a superscript ‘A’. (C) All introduced sites in pAC1A were tested by restriction digest. (D) The MfeI- and SphI-digested aph(7″) amplification product was cloned into pBAD24 digested with EcoRI (MfeI-compatible) and SphI. The MfeI site was lost in the resulting plasmid, pAC1H. (E) All restriction sites introduced to pAC1H were tested by digest.