Figure 1. Schematic of the BBB.
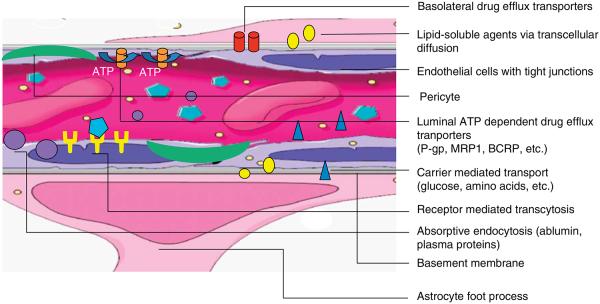
Cartoon depiction of the major components that contribute to the BBB and the pathways by which agents may access brain across the intact BBB. The major anatomical components of the BBB are: the endothelial cells with tight junctions and a specialized basement membrane, the reinforcing pericytes and the astrocytic foot processes. Transport mechanisms may include transcellular diffusion of un-bound, non-polar, lipid soluble agents (yellow circles), receptor-mediated transcytosis (turquoise hexagons), carrier-mediated transport (blue triangles) and absorptive endocytosis (purple circles). Even after successful transport across the BBB into brain via one of these mechanisms, agents may be extruded via ATP- and non-ATP-dependent drug efflux transporters (orange and red cylinders).
