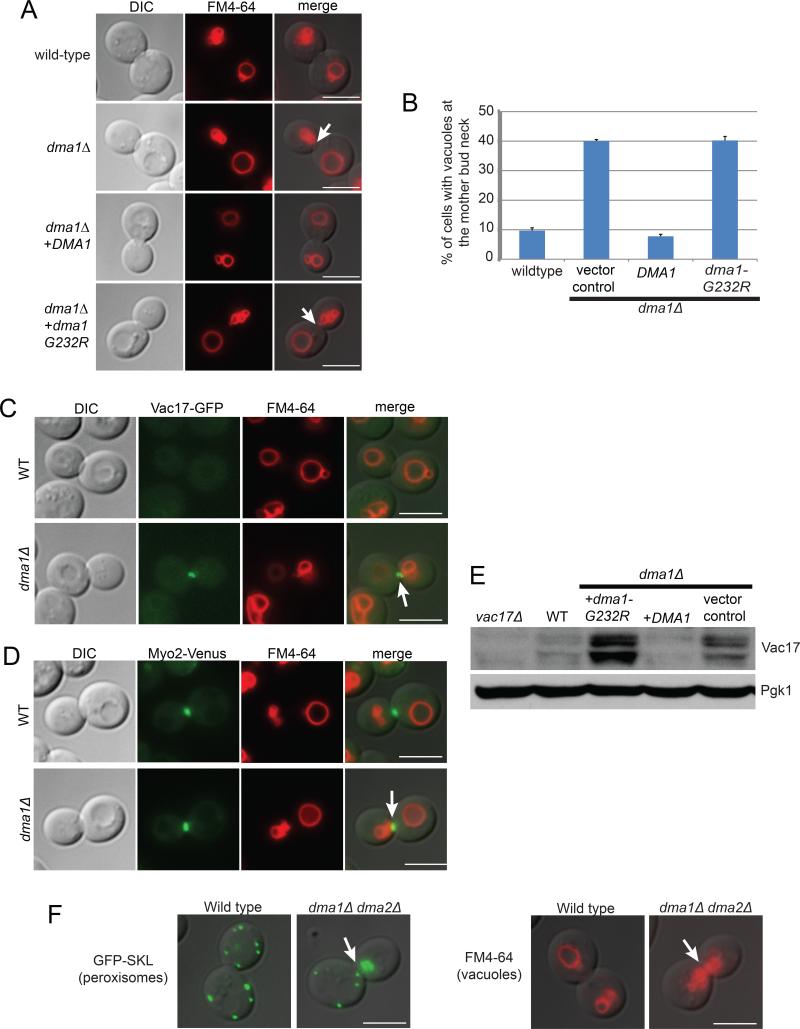
Figure 1. DMA1 is required for the termination of Myo2 dependent transport.
(A) The vacuole accumulates at the mother-bud neck in the dma1Δ mutant (arrows), expression of DMA1 but not dma1-G232R restores the proper position of the vacuole in the bud. (B) Percentage of large budded cells with the accumulation of vacuoles at the mother-bud neck in the absence of DMA1. Expression of DMA1 but not dma1-G232R restores the proper position of the bud vacuole in the dma1Δ mutant. Error bars; standard error of the mean (SEM). A minimum of 100 cells were counted per experiment for 3 experiments. (C) Vac17-GFP and vacuoles are mis-targeted to the mother-bud neck in the dma1Δ mutant. (D) The vacuole colocalizes with Myo2-Venus at the mother-bud neck in the dma1Δ mutant. (E) Vac17 levels are elevated in the dma1Δ mutant, expression of DMA1 but not dma1-G232R rescues Vac17 levels. (F) Both peroxisomes (GFP-SKL) and vacuoles (FM4-64) are mis-targeted to the mother-bud neck in large budded cells in the dma1Δ dma2Δ mutant. Bar = 5 μm. See also Figure S1.