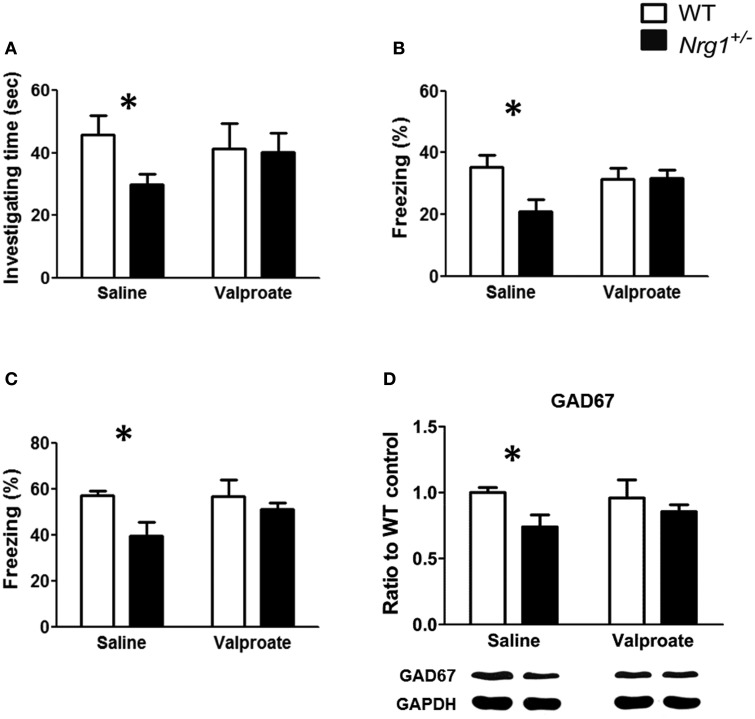
Figure 5.
The effect of chronic valproate treatment on the rescue of cognitive deficits in male wild-type (WT, white bars) and TMc-Nrg1+/− mutant (black bars) mice. Three cognitive tasks, including (A) an object recognition task, (B) a contextual fear conditioning task, and (C) a cued fear conditioning task, were conducted. Either valproate (1.5 mmol/kg, s.c.) or 0.9% saline was injected twice a day for 17 days. The object recognition task was conducted on day 16,and the contextual/cued tests of fear conditioning were performed on day 17. (D) The expression of GAD67 in the hippocampus of both WT and TMc-Nrg1+/− mice after chronic injections of either saline or valproate. Data are presented as the mean + s.e.m. *P < 0.05 between two genotypes.