Figure 2.
Zfp706 Is Required for Efficient Exit from Self-Renewal
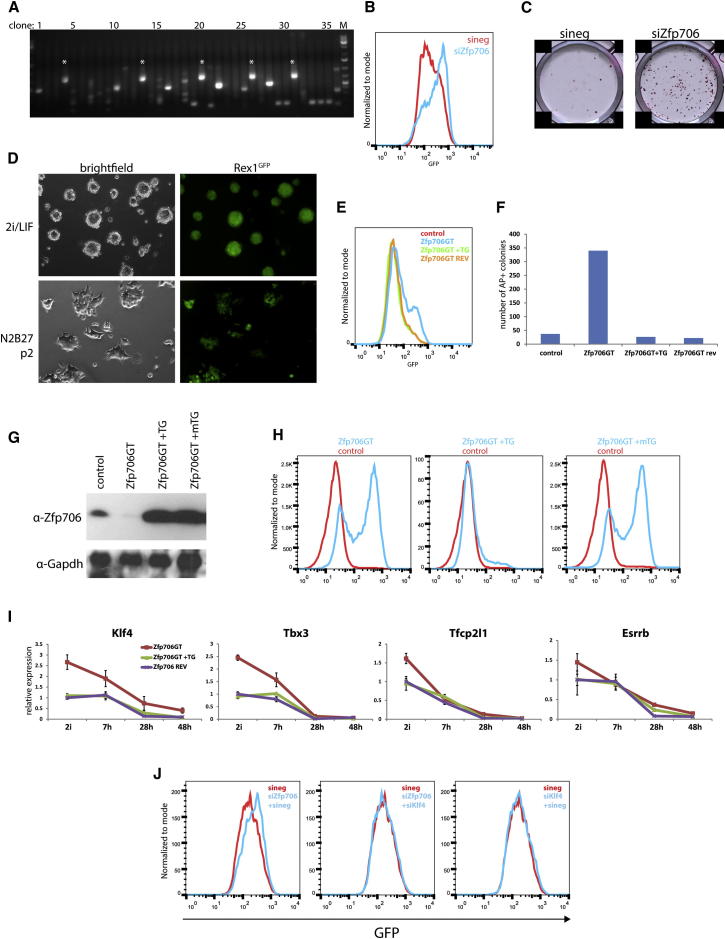
(A) Splinkerette PCR analysis of a clonal screen. Each lane corresponds to one clone; each band corresponds to one PB integration. Integrations in Zfp706 are indicated with an asterisk.
(B) Rex1GFPd2 profile 24 hr after induction of differentiation following knockdown of Zfp706 or control siRNA treatment.
(C) Commitment assay after knockdown of Zfp706 confirms a role in the exit from self-renewal. Alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining was used to visualize ESC colonies.
(D) Colony morphology and Rex1GFP expression in Zfp706GT ESCs in 2i/LIF and after two passages in N2B27.
(E) Rex1GFP profiles of Rex1GFPd2, Zfp706GT, and clonal genetic revertant (Zfp706REV) or transgene-rescued Zfp706GT (Zfp706GT+TG) ESCs after 72 hr of differentiation.
(F) Graph showing the number of AP-positive colonies generated by indicated ESC lines in a commitment assay. Colonies were counted using Image J software.
(G) Western blot of indicated cell extracts probed with indicated antibodies.
(H) Rex1GFP levels after 48 hr in N2B27 medium in control versus Zfp706GT, Zfp706GT +TG, and Zfp706 +mutant TG (mTG) ESCs.
(I) Expression kinetics of indicated genes in a differentiation time course for Zfp706GT and rescue cell lines. Mean and SEM are plotted for each time point. Expression levels were normalized to Gapdh.
(J) Rex1GFP profiles 24 hr after co-siRNA of Klf4 and Zfp706.
See also Figure S2.