Figure 1.
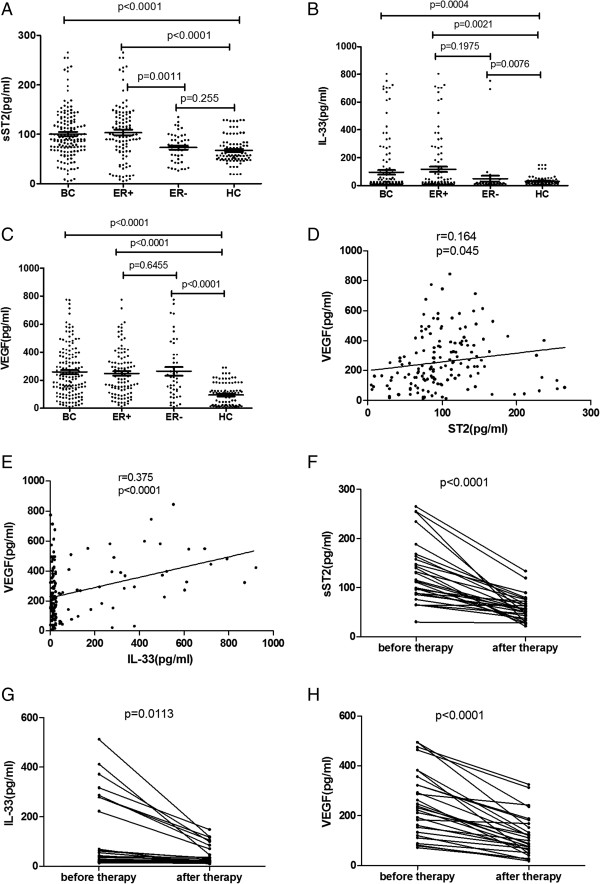
Analysis of the serum levels of sST2, IL-33 and VEGF in breast cancer patients. A. The serum levels of sST2 in breast cancer patients and the prevalence of ER-positive breast cancer patients (103/150, 68.7%) were significantly higher than those of the control group (P < 0.05, respectively). B. The serum levels of IL-33 in all breast cancer patients taken together, ER-positive breast cancer patients, and ER-negative breast cancer patients were significantly higher than those of the control group (all p < 0.05). C. The serum levels of VEGF in all breast cancer patients taken together, ER-positive breast cancer patients, and ER-negative breast cancer patients were significantly higher than those of the control group (all p < 0.05). D. The serum levels of sST2 in breast cancer patients had significant correlations with VEGF (r = 0.164, P = 0.045). E. The serum levels of IL-33 in breast cancer patients had significant correlations with VEGF (r = 0.375, P < 0.0001). F. The serum levels of sST2 significantly decreased after modified radical mastectomy (P < 0.0001). G. The serum levels of IL-33 significantly decreased after modified radical mastectomy (P = 0.0113). H. Serum levels of VEGF decreased after therapy (P < 0.0001).Abbreviations: BC=breast cancer, HC=healthy controls, ER=estrogen receptor.
