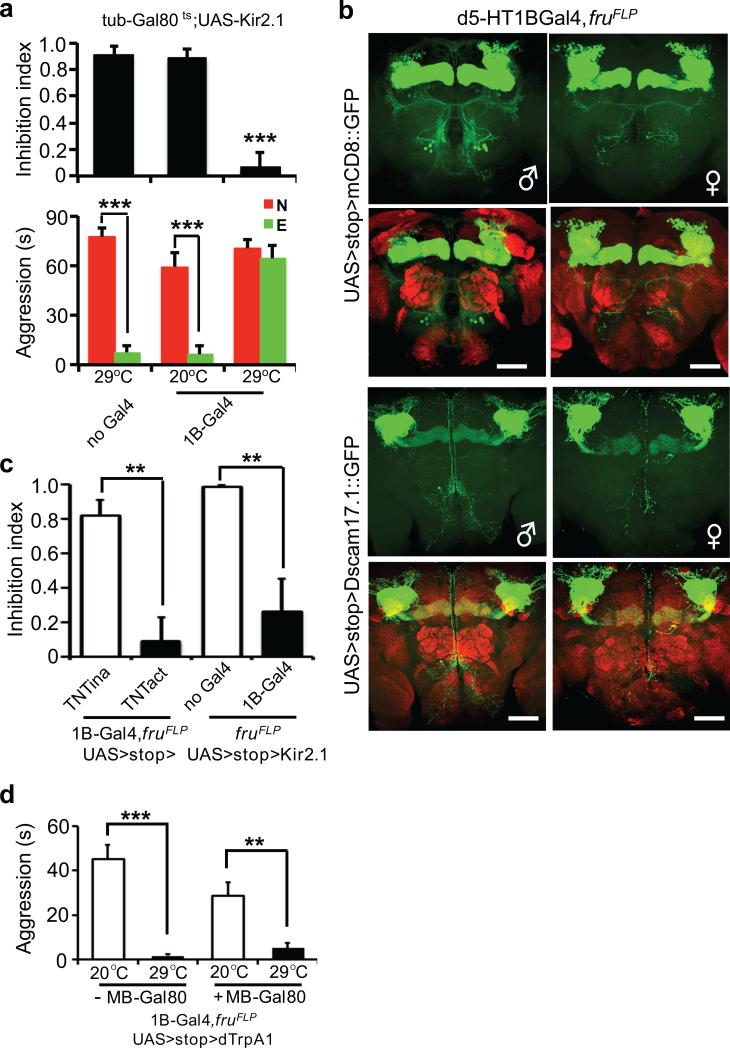
Figure 3. fru+, d5-HT1B+ sexually dimorphic neurons mediate female experience dependent inhibition of aggression.
(a) Temperature shift induced silencing of d5-HT1B+ neurons resulted in dis-inhibition of aggression, without affecting baseline aggression. (n = 5, 5 and 6 for each genotype). (b) fru+, d5-HT1B+ neurons in the adult brain labeled by mCD8::GFP and Dscam17.1::GFP, including γ-neurons of the mushroom bodies and a cluster with soma located between antennal lobes and the SOG region. The sexual dimorphism was evident with more cells and more elaborated arbors in male brains as compared to female brains. nc82 co-staining (red) showed the neuropil. Scale bar = 40 μm. (c) Blocking chemical transmission by a TNT transgene or electrically silencing by a Kir2.1 transgene expression in the fru+, d5-HT1B+ neurons led to strong dis-inhibition of aggression. (n = 6, 6, 5 and 7 for each genotype). p = 0.0012 (**), =0.0099 (**). (d) Inducible activation of fru+, d5-HT1B+ neurons by a heat-activated channel dTrpA1 led to reduced baseline aggression at 29°C as compared to the 20°C control. This reduction of baseline aggression persisted when the mushroom body neurons were excluded using MB-Gal80. The genotype for the manipulation is w+; UAS>stop>dTrpA1; fruFLP/d5-HT1B-Gal4, without or with MB-Gal80. (n = 5 for each genotype). p <0.0001 (***), =0.0049 (**). (b upper) One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. (b lower, d, e) Student's t-test. *: p<0.05, **: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001. Error bars denote s.e.m.