Abstract
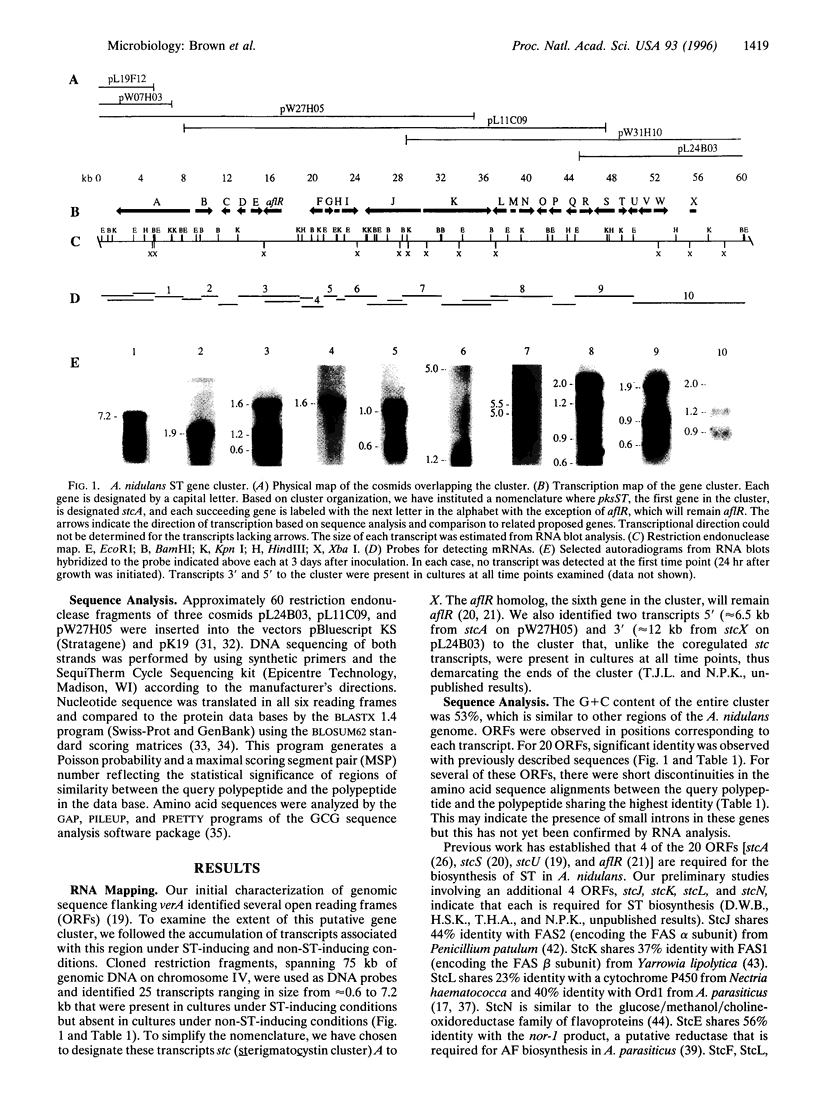
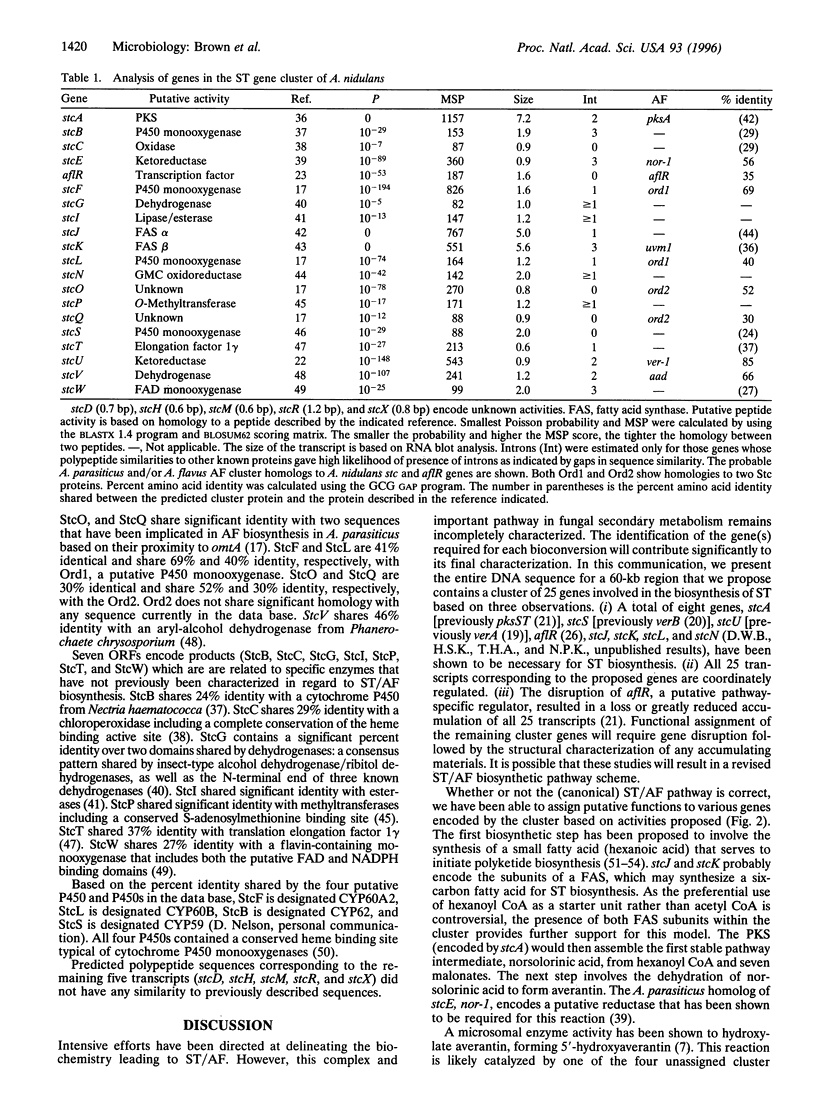
Sterigmatocystin (ST) and the aflatoxins (AFs), related fungal secondary metabolites, are among the most toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic natural products known. The ST biosynthetic pathway in Aspergillus nidulans is estimated to involve at least 15 enzymatic activities, while certain Aspergillus parasiticus, Aspergillus flavus, and Aspergillus nomius strains contain additional activities that convert ST to AF. We have characterized a 60-kb region in the A. nidulans genome and find it contains many, if not all, of the genes needed for ST biosynthesis. This region includes verA, a structural gene previously shown to be required for ST biosynthesis, and 24 additional closely spaced transcripts ranging in size from 0.6 to 7.2 kb that are coordinately induced only under ST-producing conditions. Each end of this gene cluster is demarcated by transcripts that are expressed under both ST-inducing and non-ST-inducing conditions. Deduced polypeptide sequences of regions within this cluster had a high percentage of identity with enzymes that have activities predicted for ST/AF biosynthesis, including a polyketide synthase, a fatty acid synthase (alpha and beta subunits), five monooxygenases, four dehydrogenases, an esterase, an 0-methyltransferase, a reductase, an oxidase, and a zinc cluster DNA binding protein. A revised system for naming the genes of the ST pathway is presented.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharonowitz Y., Cohen G., Martin J. F. Penicillin and cephalosporin biosynthetic genes: structure, organization, regulation, and evolution. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:461–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.002333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramayo R., Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. A large cluster of highly expressed genes is dispensable for growth and development in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):65–71. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanke S. R., Hager L. P. Chemical modification of chloroperoxidase with diethylpyrocarbonate. Evidence for the presence of an essential histidine residue. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12454–12461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomqvist K., Nikkola M., Lehtovaara P., Suihko M. L., Airaksinen U., Stråby K. B., Knowles J. K., Penttilä M. E. Characterization of the genes of the 2,3-butanediol operons from Klebsiella terrigena and Enterobacter aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(5):1392–1404. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.5.1392-1404.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody H., Griffith J., Cuticchia A. J., Arnold J., Timberlake W. E. Chromosome-specific recombinant DNA libraries from the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):3105–3109. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. GMC oxidoreductases. A newly defined family of homologous proteins with diverse catalytic activities. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 5;223(3):811–814. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90992-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler C. D. Acute care burnout and the medical record practitioner. J Am Med Rec Assoc. 1987 Jan;58(1):17–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. K., Cary J. W., Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T. E., Bennett J. W., Linz J. E., Woloshuk C. P., Payne G. A. Cloning of the Aspergillus parasiticus apa-2 gene associated with the regulation of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Oct;59(10):3273–3279. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.10.3273-3279.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. C., Peoples O. P., Walsh C. T. Acinetobacter cyclohexanone monooxygenase: gene cloning and sequence determination. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):781–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.781-789.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cove D. J. Chlorate toxicity in Aspergillus nidulans. Studies of mutants altered in nitrate assimilation. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jul 23;146(2):147–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00268083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. E., McLaren L. C. Relapsing herpes simplex encephalitis following antiviral therapy. Ann Neurol. 1983 Feb;13(2):192–195. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins A. E., Hohn T. M., McCormick S. P. Trichothecene biosynthesis in Fusarium species: chemistry, genetics, and significance. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Sep;57(3):595–604. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.3.595-604.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller G., Thiry M., Gerday C. Nucleotide sequence of the lipase gene lip2 from the antarctic psychrotroph Moraxella TA144 and site-specific mutagenesis of the conserved serine and histidine residues. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;10(5):381–388. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii K., Kurata H., Odashima S., Hatsuda Y. Tumor induction by a single subcutaneous injection of sterigmatocystin in newborn mice. Cancer Res. 1976 May;36(5):1615–1618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geever R. F., Huiet L., Baum J. A., Tyler B. M., Patel V. B., Rutledge B. J., Case M. E., Giles N. H. DNA sequence, organization and regulation of the qa gene cluster of Neurospora crassa. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):15–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90438-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Coulson A. R., Sulston J. E., Little P. F. Lorist2, a cosmid with transcriptional terminators insulating vector genes from interference by promoters within the insert: effect on DNA yield and cloned insert frequency. Gene. 1987;53(2-3):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gish W., States D. J. Identification of protein coding regions by database similarity search. Nat Genet. 1993 Mar;3(3):266–272. doi: 10.1038/ng0393-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P., Wan C. C., Billington J. A. A versiconal hemiacetal acetate converting enzyme in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Mycopathologia. 1989 Sep;107(2-3):121–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00707548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaoka S., Ogawa H., Kimura S., Gonzalez F. J. Complete cDNA sequence and cDNA-directed expression of CYP4A11, a fatty acid omega-hydroxylase expressed in human kidney. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;12(10):893–899. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Donadio S. Polyketide synthesis: prospects for hybrid antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1993;47:875–912. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.47.100193.004303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller N. P., Dischinger H. C., Jr, Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T. E., Ullah A. H. Purification of a 40-kilodalton methyltransferase active in the aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Feb;59(2):479–484. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.2.479-484.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller N. P., Kantz N. J., Adams T. H. Aspergillus nidulans verA is required for production of the mycotoxin sterigmatocystin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 May;60(5):1444–1450. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.5.1444-1450.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller N. P., Segner S., Bhatnagar D., Adams T. H. stcS, a putative P-450 monooxygenase, is required for the conversion of versicolorin A to sterigmatocystin in Aspergillus nidulans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1995 Oct;61(10):3628–3632. doi: 10.1128/aem.61.10.3628-3632.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura N., Tsuge T. Gene cluster involved in melanin biosynthesis of the filamentous fungus Alternaria alternata. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4427–4435. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4427-4435.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käfer E. Meiotic and mitotic recombination in Aspergillus and its chromosomal aberrations. Adv Genet. 1977;19:33–131. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin B. K., Anderson J. A. Purification and properties of versiconal cyclase from Aspergillus parasiticus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Feb 14;293(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90366-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maessen G. D., Amons R., Zeelen J. P., Möller W. Primary structure of elongation factor 1 gamma from Artemia. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80532-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. F. Clusters of genes for the biosynthesis of antibiotics: regulatory genes and overproduction of pharmaceuticals. J Ind Microbiol. 1992 Feb-Mar;9(2):73–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01569737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Ando Y., Hamasaki T., Yabe K. Purification and characterization of two versiconal hemiacetal acetate reductases involved in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Jul;60(7):2561–2567. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.7.2561-2567.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayorga M. E., Timberlake W. E. The developmentally regulated Aspergillus nidulans wA gene encodes a polypeptide homologous to polyketide and fatty acid synthases. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Nov;235(2-3):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00279362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. L., Miller K. Y., Roberti K. A., Timberlake W. E. Position-dependent and -independent mechanisms regulate cell-specific expression of the SpoC1 gene cluster of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):427–434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. L., Miller K. Y., Timberlake W. E. Direct and indirect gene replacements in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1714–1721. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed A. H., Chirala S. S., Mody N. H., Huang W. Y., Wakil S. J. Primary structure of the multifunctional alpha subunit protein of yeast fatty acid synthase derived from FAS2 gene sequence. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12315–12325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Kamataki T., Waxman D. J., Guengerich F. P., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Gonzalez F. J., Coon M. J., Gunsalus I. C., Gotoh O. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, accession numbers, early trivial names of enzymes, and nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Jan-Feb;12(1):1–51. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa K. E. Genetics of Aspergillus flavus: complementation and mapping of aflatoxin mutants. Genet Res. 1979 Aug;34(1):1–9. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300019236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa K. E. Linkage groups in Aspergillus flavus. Mycologia. 1976 Jan-Feb;68(1):159–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. A., Nystrom G. J., Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T. E., Woloshuk C. P. Cloning of the afl-2 gene involved in aflatoxin biosynthesis from Aspergillus flavus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):156–162. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.156-162.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. H., Hohn T. M., McCormick S. P. Reduced virulence of Gibberella zeae caused by disruption of a trichothecene toxin biosynthetic gene. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1995 Jul-Aug;8(4):593–601. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-8-0593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimmann C., VanEtten H. D. Cloning and characterization of the PDA6-1 gene encoding a fungal cytochrome P-450 which detoxifies the phytoalexin pisatin from garden pea. Gene. 1994 Sep 2;146(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser J., Muheim A., Hardegger M., Frank G., Fiechter A. Aryl-alcohol dehydrogenase from the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Gene cloning, sequence analysis, expression, and purification of the recombinant enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 11;269(45):28152–28159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer E., Köttig H., Regler R., Rottner G. Genetic control of Yarrowia lipolytica fatty acid synthetase biosynthesis and function. J Basic Microbiol. 1988;28(5):283–292. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3620280502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skory C. D., Chang P. K., Cary J., Linz J. E. Isolation and characterization of a gene from Aspergillus parasiticus associated with the conversion of versicolorin A to sterigmatocystin in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Nov;58(11):3527–3537. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3527-3537.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skory C. D., Chang P. K., Linz J. E. Regulated expression of the nor-1 and ver-1 genes associated with aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 May;59(5):1642–1646. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1642-1646.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. J., Williams D. H. On the evolution of functional secondary metabolites (natural products). Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(1):29–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trail F., Chang P. K., Cary J., Linz J. E. Structural and functional analysis of the nor-1 gene involved in the biosynthesis of aflatoxins by Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Nov;60(11):4078–4085. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.11.4078-4085.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trail F., Mahanti N., Rarick M., Mehigh R., Liang S. H., Zhou R., Linz J. E. Physical and transcriptional map of an aflatoxin gene cluster in Aspergillus parasiticus and functional disruption of a gene involved early in the aflatoxin pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1995 Jul;61(7):2665–2673. doi: 10.1128/aem.61.7.2665-2673.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vining L. C. Secondary metabolism, inventive evolution and biochemical diversity--a review. Gene. 1992 Jun 15;115(1-2):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90551-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wogan G. N. Aflatoxins as risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma in humans. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7 Suppl):2114s–2118s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woloshuk C. P., Foutz K. R., Brewer J. F., Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T. E., Payne G. A. Molecular characterization of aflR, a regulatory locus for aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Jul;60(7):2408–2414. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.7.2408-2414.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Ando Y., Hashimoto J., Hamasaki T. Two distinct O-methyltransferases in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2172–2177. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2172-2177.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Hamasaki T. Stereochemistry during aflatoxin biosynthesis: cyclase reaction in the conversion of versiconal to versicolorin B and racemization of versiconal hemiacetal acetate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Aug;59(8):2493–2500. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.8.2493-2500.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Nakamura Y., Nakajima H., Ando Y., Hamasaki T. Enzymatic conversion of norsolorinic acid to averufin in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1340–1345. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1340-1345.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J. H., Leonard T. J. Sterigmatocystin biosynthesis in Aspergillus nidulans requires a novel type I polyketide synthase. J Bacteriol. 1995 Aug;177(16):4792–4800. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.16.4792-4800.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Cary J. W., Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T. E., Keller N. P., Chu F. S. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA from Aspergillus parasiticus encoding an O-methyltransferase involved in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Nov;59(11):3564–3571. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.11.3564-3571.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Chang P. K., Cary J. W., Wright M., Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T. E., Payne G. A., Linz J. E. Comparative mapping of aflatoxin pathway gene clusters in Aspergillus parasiticus and Aspergillus flavus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1995 Jun;61(6):2365–2371. doi: 10.1128/aem.61.6.2365-2371.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



