Figure 1.
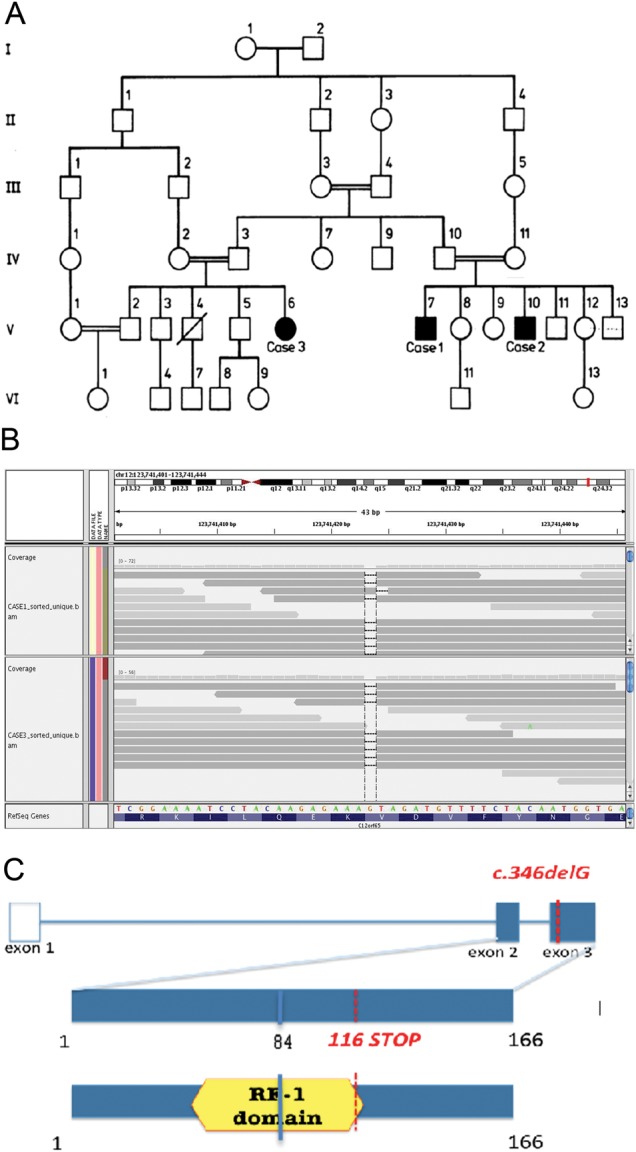
Pedigree of the family and the C12orf65 p.V116X mutation. (A) Pedigree of the family. A square represents a male person and a circle represents a female person. A double horizontal line indicates parental consanguinity. Black symbols indicate affected members with Charcot–Marie Tooth type 2 (CMT2) and optic atrophy in whom a neurological exam was performed; blank symbols show unaffected family members. A diagonal line marks deceased individuals. This pedigree has been reported elsewhere.25 (B) Upper panel: whole-exome sequencing data for the p.V116X mutation in C12orf65. The aligned reads viewed through the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) viewer (http://www.broadinstitute.org/igv/). Reads are depicted as arrows (grey bands). A coverage histogram per base is shown above the reads. RefSeq gene (over the C12orf65 gene) is represented in the lower part both as amino acid sequence (blue) and as reference sequence: green, A; orange, G; red, T; blue, C. Dashes represent the deleted base. Note the drop of coverage (black arrow) over the dashed base, representing the G base deleted in both samples. (C) Schematic diagram of the C12orf65 gene and protein. The position of the mutation in the patient DNA and the position of the resulting premature stop codon are indicated in red; blue indicates the mutation and the position of the resulting stop codon described in patients with severe encephalomyopathy.
