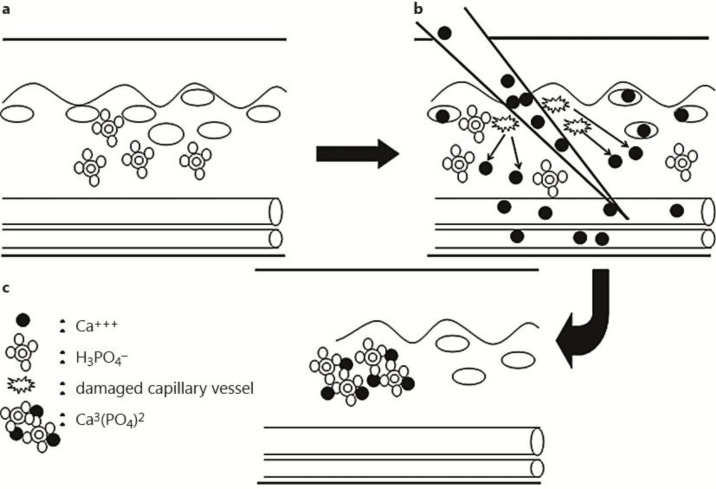
Fig. 4.
Proposed mechanism of iatrogenic calcinosis cutis. a Before treatment: tissue injury induced by introduction of the needle causes capillary disruption in the dermis with calcium ion release (b). c The released calcium binds to phosphate in the dermis, with resultant deposition of calcium phosphate crystals in the dermis.