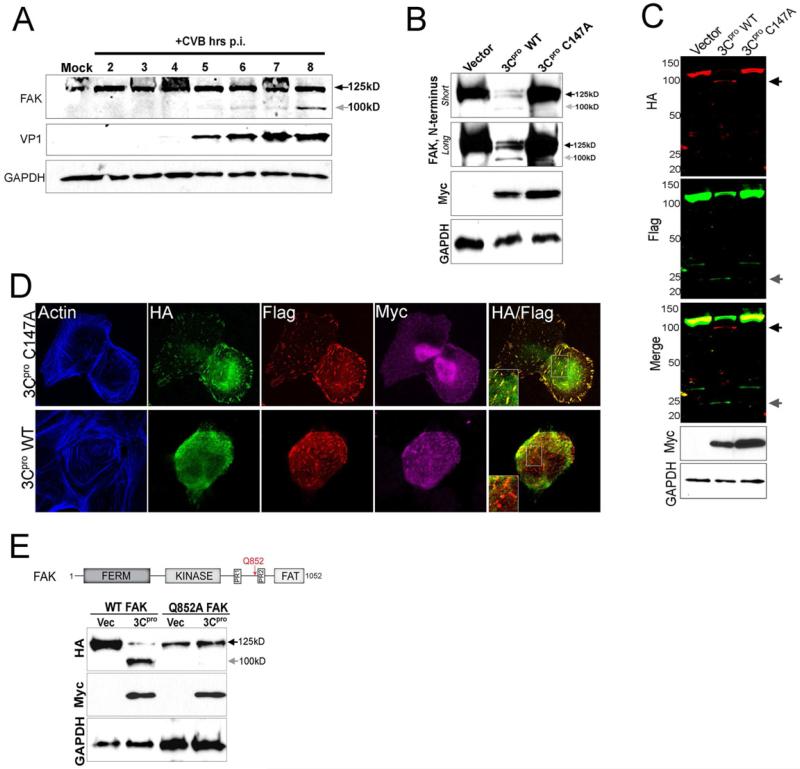
Figure 5. CVB Infection Induces FAK Cleavage by 3Cpro.
(A), Immunoblot analysis of FAK (using an antibody directed against the N-terminus, top) and VP1 (middle) in Caco-2 cells infected with CVB for the times shown. Grey arrow denotes a CVB-induced cleavage fragment of ~ 100 kD. Immunoblotting for GAPDH (bottom) is included as a loading control. (B), Immunoblot analysis for endogenous FAK using an antibody directed against the N-terminus in cells transfected with vector or Myc-tagged wild-type (WT) or C147A 3Cpro. Immunoblotting for GAPDH (bottom) is included as a loading control. (C), Dual-color immunoblot analysis using a LI-COR Odyssey infrared imaging system and antibodies specific for HA (700nm, red) and Flag (800nm, green) in HEK293 cells transfected with vector, Myc-3Cpro wild-type or C147A, and HA-FAK-Flag. Black arrows denote full-length and cleavage fragments. An overlay of both channels is shown below (with yellow indicating overlapping signals). (D), Confocal microscopy from U2OS cells transfected with Myc-wild-type (WT) or mutant (C147A) 3Cpro and HA-FAK-Flag. Cells were fixed 48 h following transfection and stained for HA (green), Flag (red), Myc (purple), and actin (blue). Areas of colocalization appear as yellow. (E), Top, schematic of full-length FAK indicating the location of the FERM, kinase, and FAT domains, two proline-rich regions, and the location of a 3Cpro-mediated cleavage site at position Q852 (red arrow). Bottom, immunoblot analysis for HA-FAK (top) and Myc (bottom) in cells transfected with either WT or mutant FAK (Q852A) and vector control or Myc-WT 3Cpro. Grey arrow denotes the presence of a ~ 100 kD cleavage fragment.