Fig. 3.
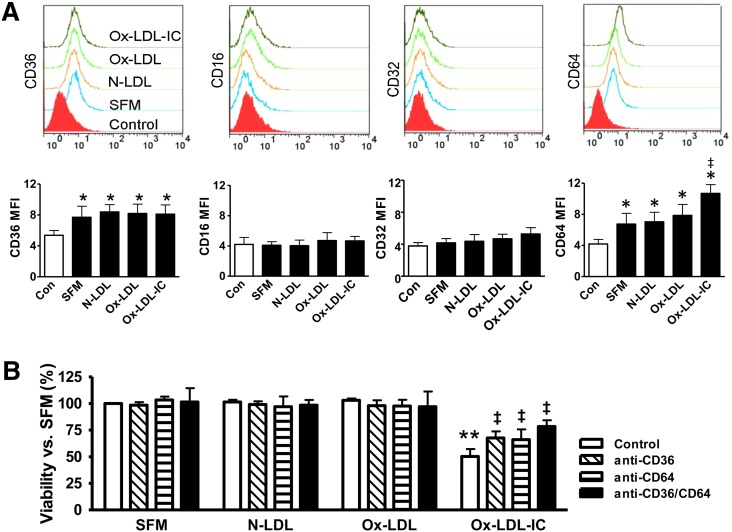
Pericyte surface receptors and effects of ox-LDL-ICs. A: Receptor expression in pericytes. Cells were treated for 6 h with 50 mg/l N-LDL, ox-LDL, ox-LDL-ICs, or SFM, and labeled with FITC-tagged antibodies against CD16, CD32, CD36, or CD64 for flow cytometry. IgG or IgM were used, as appropriate, as nonbinding baseline controls. Mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs) in response to N-LDL, ox-LDL, or ox-LDL-ICs were compared with nonbinding baseline control and SFM (mean ± SD, n = 3; *P < 0.05 vs. nonbinding baseline, indicative of receptor expression; ‡P < 0.05 vs. SFM). CD36 and CD64 were expressed, but not CD16 or CD32. Ox-LDL-ICs increased CD64 (but not CD36) expression versus SFM. Neither ox-LDL nor N-LDL altered CD64 or CD36 expression. B: Receptor-mediated cytotoxicity. Cell viability was measured by the CCK-8 assay after 24 h treatment with 50 mg/l N-LDL, ox-LDL, or ox-LDL-ICs versus SFM. Ox-LDL-ICs significantly reduced pericyte viability; the effects were attenuated by the blocking antibodies against CD36 and CD64. Blockade of both receptors together offered additional protective effects. Data are expressed as percentage of SFM control (mean ± SD, n = 3). **P < 0.01 versus SFM; ‡P < 0.05 versus ox-LDL-IC treatment alone.