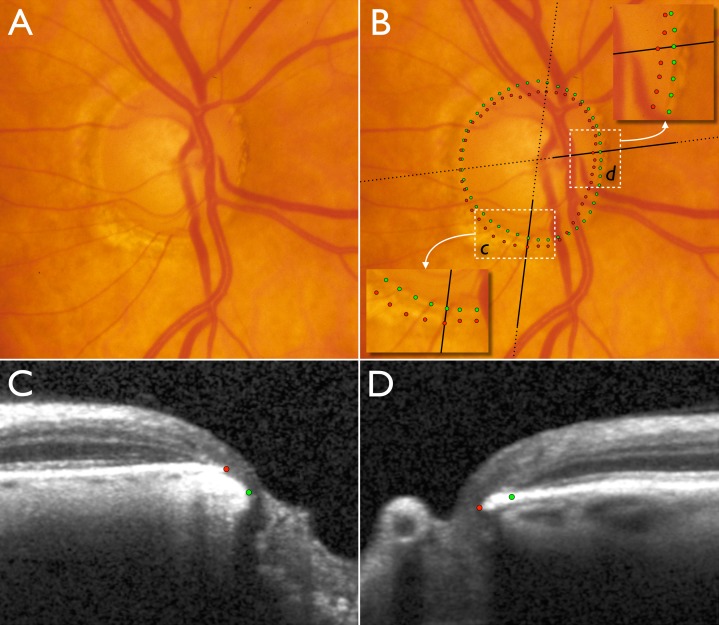
Figure 2.
Disc photograph and two (of 24) SD-OCT radial B-scans of the right optic nerve head of a glaucoma patient. (A) Disc photograph with localized cupping and apparently very little or no neuroretinal rim remaining in the inferotemporal sector. (B) Clinical DM positions obtained from examination of stereo disc photographs (green) and projected BMO (red) positions obtained from SD-OCT scans. Insets show magnified areas in c and d. Dotted black lines indicate the orientation of the radial B-scans and bold solid black lines indicate the section of the B-scans shown in C and D. (C) B-scan corresponding to inset c. (D) B-scan corresponding to inset in d. In the inferotemporal section (c and C), BMO is external to DM. In this quadrant, SD-OCT detects rim tissue that is not clinically evident in the photograph. In the nasal section (d and D), BMO is internal to DM and SD-OCT detects a narrower rim than clinically apparent.