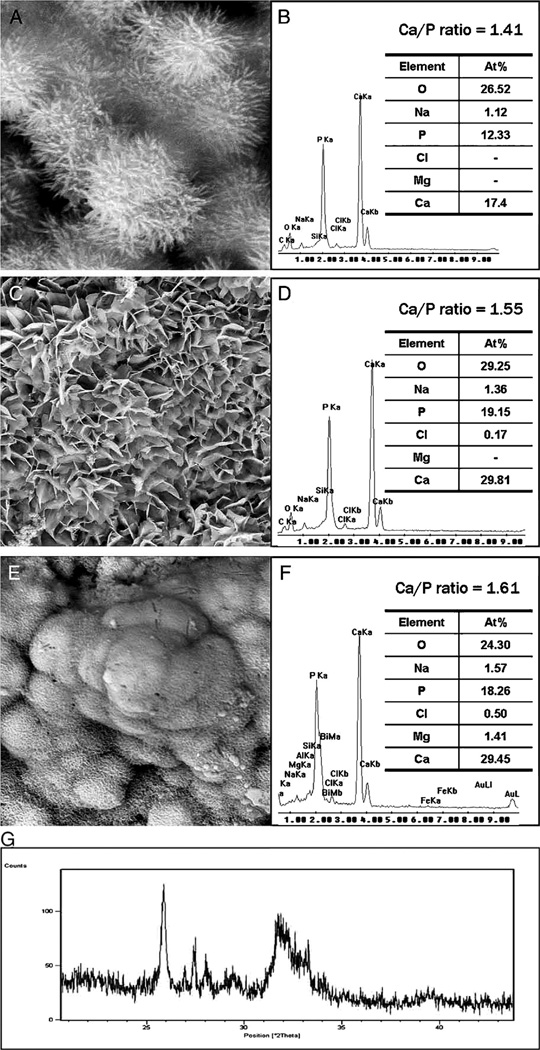
Fig. 4.
Characterization of precipitates formed by MTA BIO after 2 months of immersion in phosphate-buffered saline. (A) SEM image showing the acicular nature of spherules (original magnification, 8000×). (B) Energy dispersive X-ray (EDAX) spectrum for precipitates in (A) and semi-quantitative chemical composition showing their Ca/P molar ratio. (C) SEM image showing petal-like precipitates (original magnification, 1000×). (D) EDAX spectrum for precipitates in (C) revealed a greater Ca/P molar ratio and lattice substitution of Na and Cl. (E) SEM image of compact lath-like precipitates (original magnification, 1000×). (F) Semi-quantitative analysis of the EDAX data derived from (E) indicates that the precipitates have a Ca/P molar ratio of 1.61 with lattice substitution of Na, Cl, and Mg. (G) X-ray diffraction pattern of the calcium phosphate precipitates obtained after 2 months of immersion in phosphate-buffered saline, revealing the presence of poorly crystalline apatite.
Reproduced from Reyes-Carmona et al.86, with permission from the publisher.