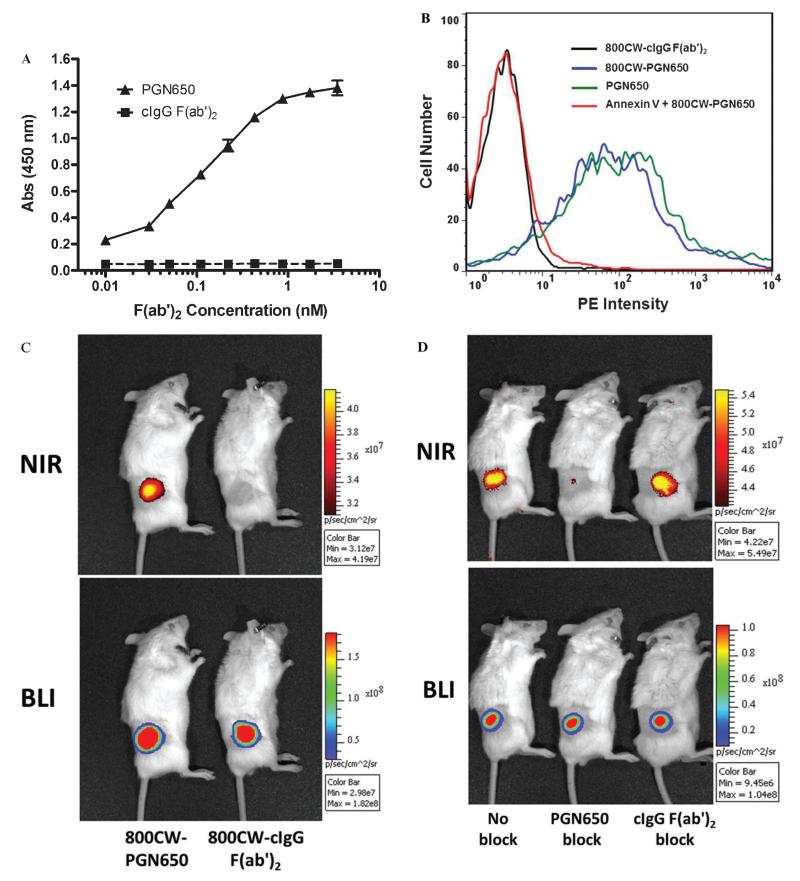
Figure 1.
Targeting of PGN650 to phosphatidylserine (PS). A, In vitro targeting of PGN650 to PS on plastic surfaces by ELISA. PS was coated onto a 96-well plastic microplate. Following a blocking step, the primary antibody and control IgG were plated on the assay plate in serial 1:1 dilutions. Wells were washed and incubated with peroxidase-conjugated goat antihuman IgG antibody. Wells were washed and developed with a peroxidase substrate, and the colorimetric reaction was measured by a spectrophometric plate reader. Abs = absorbance. B, Targeting of PGN650 to PS on cell surface membranes. Jurkat cells treated with etoposide were incubated for 30 minutes with 10 μg of 800CW-PGN650, 10 μg of 800CW-PGN650 + 10 μg of annexin V, 10 μg of unlabeled PGN650, or 10 μg of 800CW-cIgG F(ab′)2. Following a second incubation with a 1:100 dilution of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)-conjugated goat antihuman F(ab′)2 antibody for 30 minutes, cells were washed and subjected to FACS analysis. C, In vivo targeting of PGN650 to PS in tumors. Mice bearing subcutaneous PC-3luc tumors were injected intravenously with 1 mg/kg of 800CW-PGN650 or 800CW-cIgG F(ab′)2 fragments and imaged 24 hours after injection. Near-infrared (NIR) optical images are shown in the upper panel and bioluminescent images (BLIs) are shown in the lower panel. D, Specific blocking of 800CW-PGN650 targeting in vivo. PC-3luc tumor-bearing animals were untreated or injected with a 50-fold excess of unlabeled PGN650 or unlabeled cIgG F(ab′)2 10 minutes prior to injection with 1.0 mg/kg of 800CW-PGN650. NIR optical images are shown in the upper panel and BLIs are shown in the lower panel.