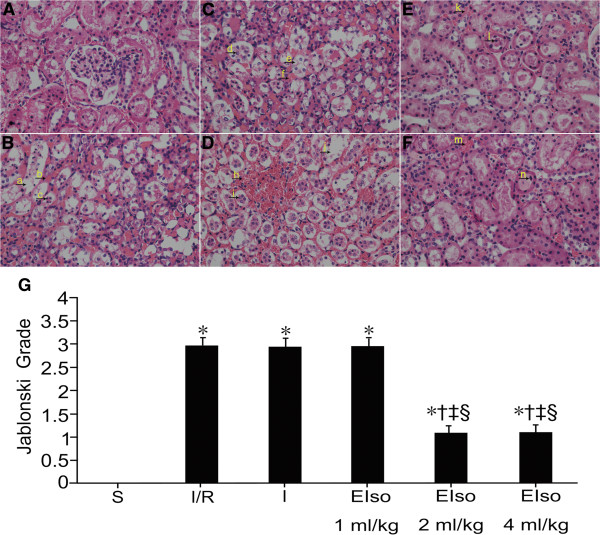
Figure 1.
Renal injury panels (A) to (F) are representative micrographs of optical microscopic analysis in the renal cortex of rats for the sham (S), I/R, intralipid (I) and EIso groups (EIso 1, 2 or 4 ml/kg), respectively. Normal kidney tissue, normal histological characteristic of glomeruli and tubules were observed in the sham group (A). In the I/R (B), intralipid (C) and 1 ml/kg EIso (D) groups, marked structural changes were seen in kidney tissues. Arrow a and j indicate tubular dilatation; Arrow b, f and h indicate interstitial hemorrhage; Arrow c, d and i indicate sloughing tubular epithelial cell necrosis; Arrow e indicates tubular epithelial cell vacuolar degeneration. Moderate kidney damages were showed in the 2 (E) and 4 (F) ml/kg EIso groups. Arrow k and m indicate interstitial hemorrhage; Arrow l and n indicate sloughing tubular epithelial cell necrosis. Original magnification × 400. Panel (G) represents Jablonski grade of histological appearance of acute tubular necrosis. The type and severity of acute tubular necrosis was graded from 0 to 4 in each group of rats (see Table 1). Kidneys subjected to 45 min ischemia and 3 h reperfusion increased Jablonski grade as compared to the sham group. Both 2 and 4 ml/kg EIso pretreatment reduced Jablonski grade as compared to the I/R, intralipid and 1 ml/kg EIso groups. *P < 0.05 compared to S, †P < 0.05 compared to I/R, ‡P < 0.05 compared to I, §P < 0.05 compared to EIso 1 ml/kg.