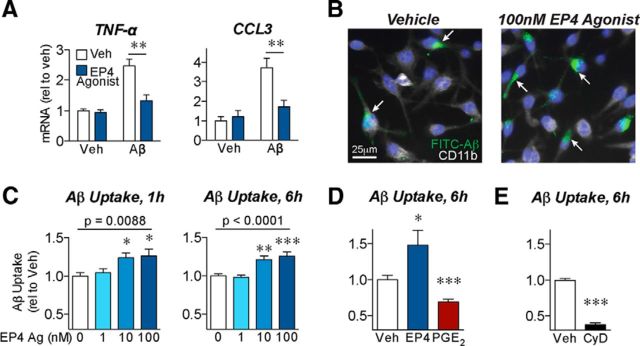
Figure 2.
EP4 receptor signaling reduces inflammatory responses and promotes phagocytosis of Aβ42 by BV2 microglial cells. A, BV2 microglial cells were cotreated with oligomeric Aβ42 (5 μm) or the EP4 agonist AE1–329 (100 nm) for 6 h. qRT-PCR demonstrates that EP4 receptor stimulation attenuates the expression of the cytokine TNF-α and the chemokine CCL3 in response to Aβ42. n = 5 or 6 independent samples per group. **p < 0.01 (Bonferroni multiple comparison test). B–E, BV2 microglial cells were pretreated for 3 h with the EP4 agonist AE1–329, PGE2, or the phagocytosis inhibitor cytochalasin-D before addition of FITC-labeled Aβ (1 μm) for the indicated times. B, Images of BV2 cells immunostained for CD11b (white) and nuclei (Hoechst, blue) demonstrate that pretreatment with EP4 agonist (3 h, 100 nm) increases uptake of FITC-Aβ42 (6 h, internalized Aβ indicated with arrows). C, EP4 agonist pretreatment dose-dependently increases intracellular FITC-Aβ42 levels after either 1 or 6 h of FITC-Aβ42 incubation. n = 12 (1 h) or 7 (6 h) samples per group. p (one-way ANOVA). *p < 0.05, versus vehicle treatment (Dunnett's post test). **p < 0.01, versus vehicle treatment (Dunnett's post test). ***p < 0.001, versus vehicle treatment (Dunnett's post test). D, EP4 agonist (100 nm) treatment increases, whereas PGE2 (100 nm) treatment decreases, intracellular FITC-Aβ42 levels after 6 h. E, Cytochalasin-D (CyD, 2 μm) decreases intracellular FITC-Aβ42 levels after 6 h. D, E, n = 7 or 8 samples per group. *p < 0.05, versus vehicle treatment (unpaired t test). ***p < 0.001, versus vehicle treatment (unpaired t test).