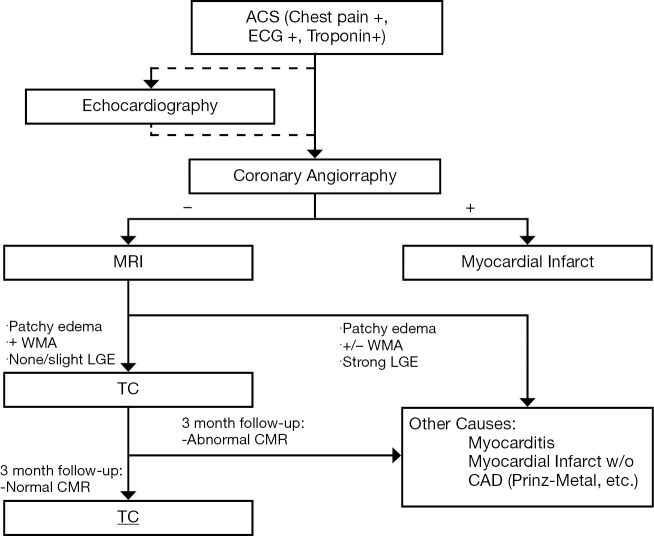
Figure 3.
Established workflow at our institution. When a patient presents with a confirmed ACS (Chest pain, ECG + and Troponin +) a coronary angiography is performed. Before the angiography and at the patient’s bedside an echocardiography is usually performed (although considered optional) in order to start risk stratifying the patient and coming up with possible differentials. If the angiography is concordant with the clinical and echocardiographic findings an MI is diagnosed and further studying of the patient ceased. If the angiography findings are discordant an MR is performed. In light of the MR findings the patient will be classified as a probable TC, to be confirmed through a three months follow-up MR, or will be classified into another set of diseases that can present as an ACS. Abbreviations: ACS, acute coronary syndromes; MI, myocardial infarction; TC, takotsubo cardiomyopathy.