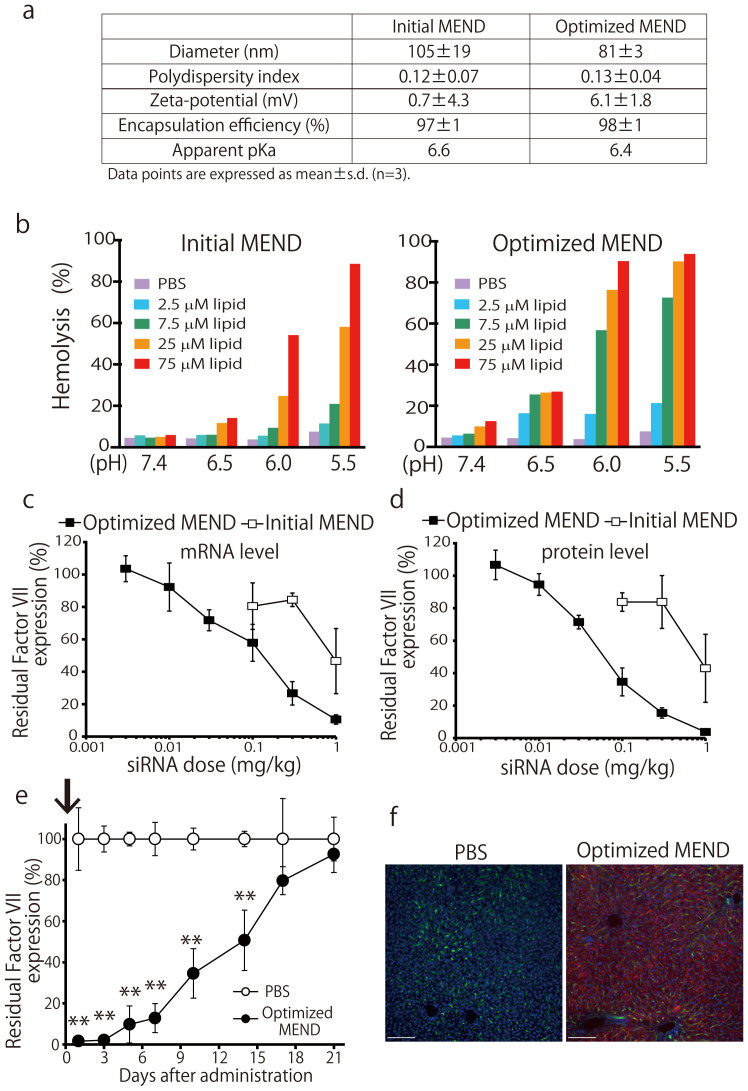
Figure 3. In vitro and in vivo characterization of the optimized MEND.
(a) Physical properties of multifunctional envelope-type nano devices (MENDs). (b) The membrane fusion activity of initial and optimized MENDs was assessed by an in vitro hemolysis assay. Values (normalized to hemolysis with known lysing agent (Triton)) are presented as the mean (n = 3). N.C.; negative control (treated with PBS). (c, d) In vivo hepatic Factor VII mRNA (c) and serum Factor VII protein (d) levels at 48 hr after the administration of the initial and optimized MENDs. Data points are presented as the mean ± s.d. (n = 3) of values normalized to those obtained with uninjected mice. (e) In vivo persistence of knockdown was investigated by monitoring serum Factor VII levels at the indicated number of days after administration of optimized MENDs at a dose of 1.0 mg siRNA per kg. **P<0.01. Data points are presented as the mean ± s.d. (n = 3) of values normalized to those obtained with uninjected mice. (f) Liver tissues were collected after single injection of PBS or the optimized MENDs encapsulating Cy5-siRNA (red) and stained with FITC-isolectin B4 (green) and Hoechst33342 (blue) to detect blood vessels and nuclei (respectively). Bars represent 100 μm.