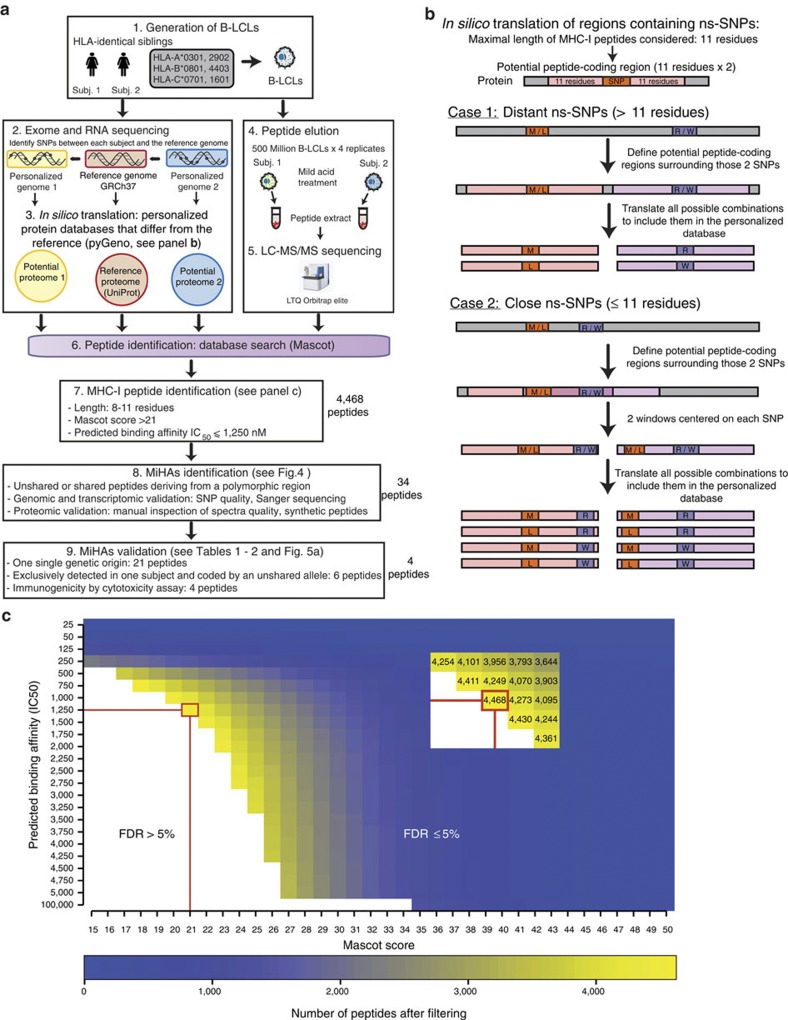
Figure 1. High-throughput genoproteomic strategy used for the identification of polymorphic MIPs on B-LCLs from two HLA-identical siblings.
(a) General overview of the personalized approach, which combines next-generation sequencing, MS and bioinformatics. (b) Schematic representation of the combinatorial method used to translate in silico polymorphic regions containing ns-SNPs. (c) Combining the predicted MHC-binding affinity and Mascot score enables to discriminate between MIPs and contaminant peptides. The data set of peptides identified with an FDR≤5% was filtered according the Mascot score (which represents the confidence level of a peptide assignation), and the predicted MHC-binding affinity. The red rectangle and lines indicate the combination of values (IC50≤1,250 nM and Mascot score ≥21) that allowed identifying the maximum number of MIPs with a 5% FDR threshold.