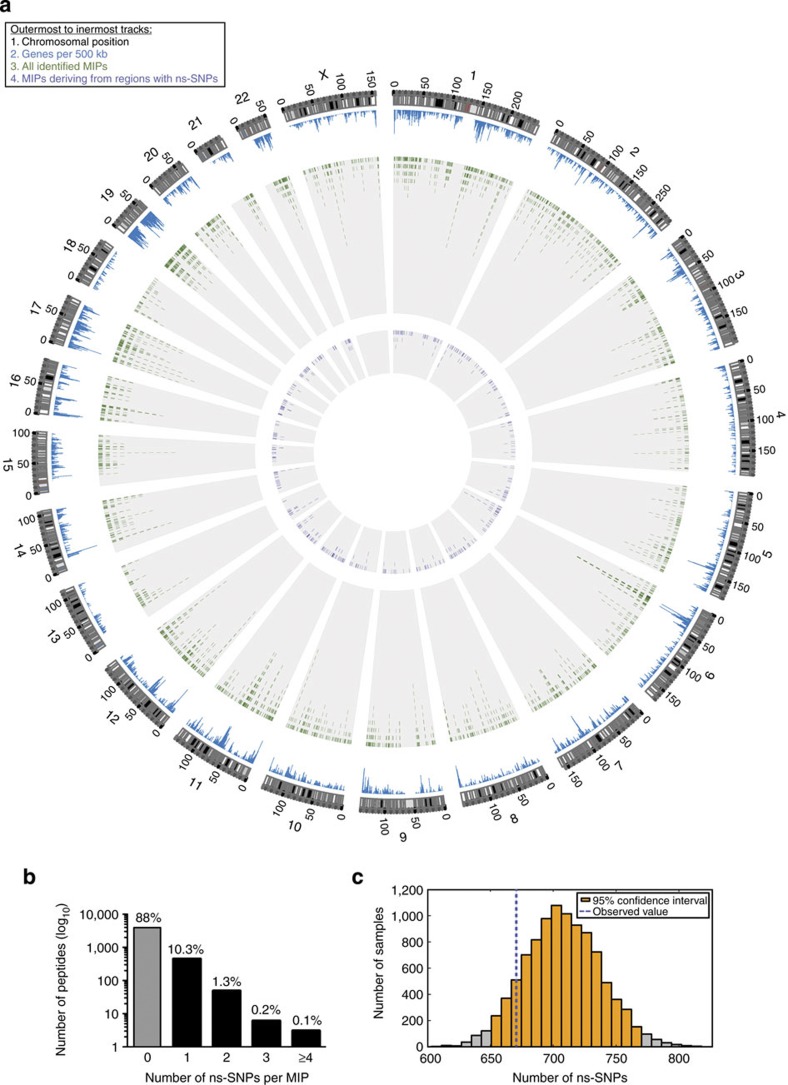
Figure 6. Frequency of ns-SNPs in the MIP-coding exome.
(a) Circos plot illustrates the relative proportion of polymorphic MIPs (n=536) in the immunopeptidome and the genomic location of their coding loci. (b) Histogram showing the number and percentages of MIP-coding regions containing ns-SNPs in the global population. We used dbSNP to find validated ns-SNPs in the exomic sequences encoding the 4,468 MIPs identified in our subjects. In the case of MIPs deriving from multiple source regions, the average number of ns-SNPs of all possible MIP source regions was calculated. (c) The 4,468 MIPs of our subjects were encoded by 13,404 nucleotides. We performed 10,000 random samplings of 4,468 exomic sequences (containing a total of 13,404 nucleotides) from the human reference exome (Ensemble GRCh37.65). In all samplings, the frequency of exomic sequences coding for 8-,9-,10- and 11-mers was identical to the frequency found in the 4,468 MIP-coding sequences from our subjects. The histogram depicts the distribution of validated ns-SNPs (dbSNP) in exomic sequences from the global population found in 10,000 random samplings of the whole exome. The average number of ns-SNPs of all random samplings was 708 (s.d.: 30.4, 95% confidence interval: 650–768 shown in orange). The blue dotted line shows the number of ns-SNPs (n=670) in the exomic sequences coding for the MIPs detected in our subjects.