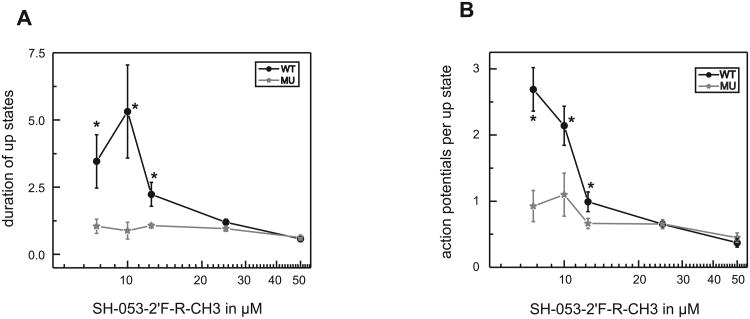
Figure 3.
Concentration-dependent effects of SH-053-2′F-R-CH3 on the duration of up states and on the number of action potentials during up states in cultured cortical neurons from wild type and 5 (H105R) knock-in mice.
(A) The duration of up states is increased by low concentrations of SH-053-2′F-R-CH3 in wild type slices. Values are presented as duration of up states in the presence of SH-053-2′F-R-CH3 divided by duration of up states under control condition. SH-053-2′F-R-CH3 leads to an increase in the wild type (black dots) by 3.5 ± 1.0 at 7.5 μM, by 5.3 ± 1.7 at 10 μM, and by 2.2 ± 0.4 at 12.5 μM, respectively. In cultured slices from the 5(H105R) mutant (grey stars) this effect is absent. * significantly different from 5(H105R) mutant (P < 0.05, t-test).
(B) Low concentrations of SH-053-2′F-R-CH3 lead to an increased number of action potentials during up states in wild type slices. The values are given as number of action potentials during up state in the presence of SH-053-2′F-R-CH3 divided by control condition. SH-053-2′F-R-CH3 increases the number of action potentials during up state in the wild type (black dots) by 2.7 ± 0.3 at 7.5 μM and by 2.1 ± 0.3 at 10 μM, respectively. In slices from the 5(H105R) mutant (grey stars) no such increase is present. * significantly different from 5(H105R) mutant (P < 0.05, t-test). At higher concentrations SH-053-2′F-R-CH3 reduces the number of action potentials during up states in both, wild type and 5(H105R) mutant slices.