Figure 5.
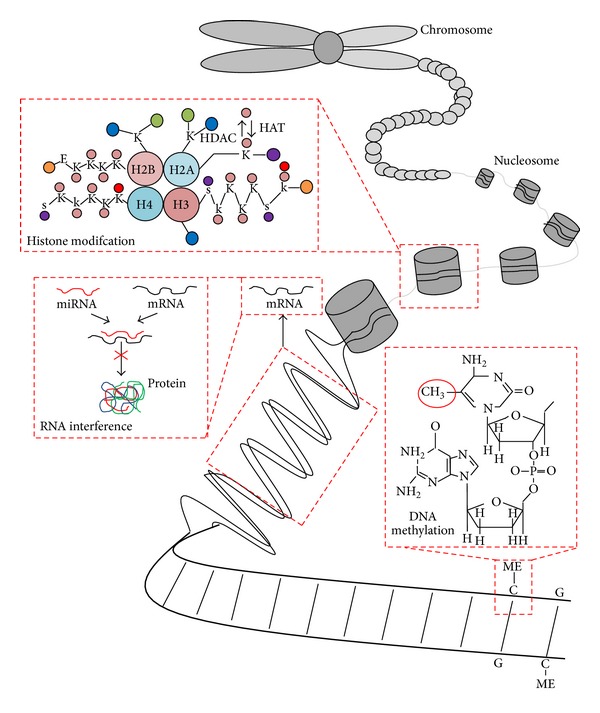
Mechanisms of epigenetic regulation. Three main forms of epigenetic modification include histone modification, RNA interference, and DNA methylation. Histone (chromatin) modification refers to the covalent posttranslational modifications to the N-terminal tails of the four core histone proteins; this modification is commonly acetylation/deacetylation changes at lysine residues mediated by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs). RNA interference is predominantly mediated through microRNAs, which inhibit the translation of mRNA into protein. DNA methylation occurs at cytosine residues of CpG dinucleotides and acts to regulate gene expression. Pink circle = acetyl group, purple circle = phosphate group, red circle = methyl group, blue circle = carboxyl terminus, green circle = ubiquitin, orange circle = amino terminus, k = lysine, E = glutamic acid, S = serine. H2A, histone 2A; H2B, histone 2B; H3, histone 3; H4, histone 4.
