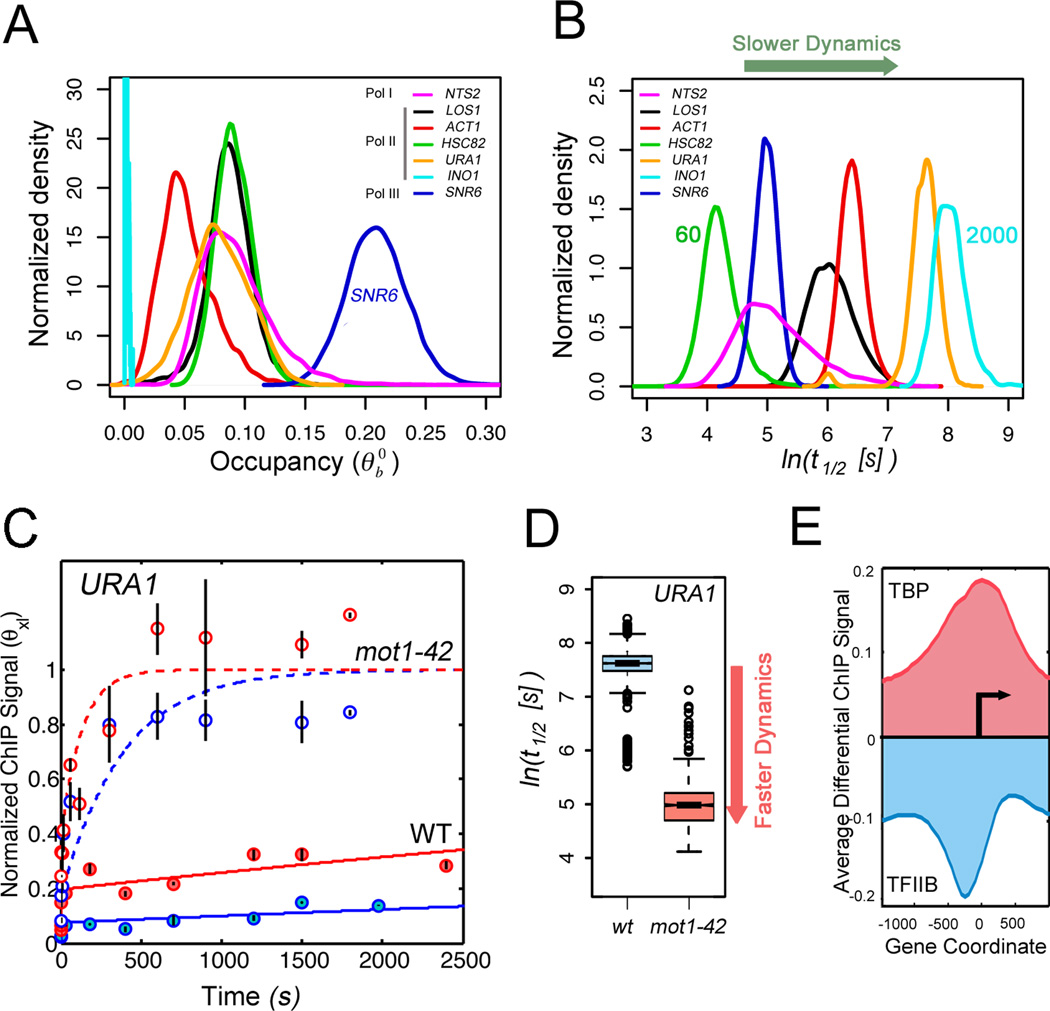
Figure 4. TBP dynamics and regulation by Mot1.
(A) Distributions of TBP occupancy at different yeast promoters obtained by multiple independent fits of the CLK data (7). (B) Distributions of TBP-promoter half-lives (7), whose mean values vary from 60 to about 2000 seconds. (C) Model fits of CLK data for TBP binding to the Mot1-activated URA1 promoter in WT (sold lines) and mot1-42 cells (dashed lines). Data and fits from cells expressing WT levels of TBP are shown in blue, results from cells over-expressing TBP are in red. (D) Boxplots for distribution of t1/2 values (log scale) for TBP binding to the Mot1-activated URA1 promoter in WT (blue) and mot1-42 cells (red). (E) Average genome-wide log2 differential TBP and TFIIB ChIP-chip signals at promoters in mot1-42 versus WT cells shown with respect to the transcription start site (arrow) (7).