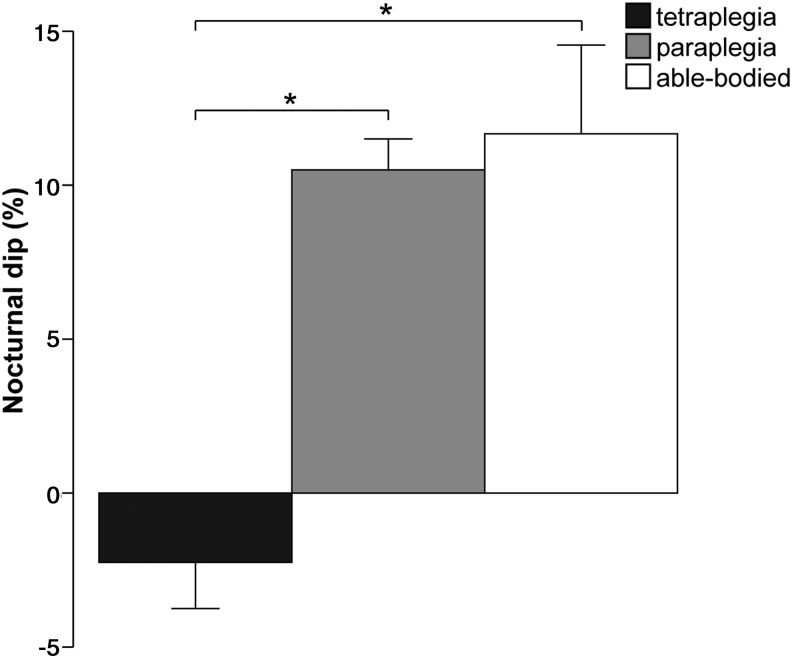
FIG. 3.
Nocturnal dip differences of systolic blood pressure among tetraplegic (C4-C8, American Spinal Injury Association Impairment Scale [AIS] A, n=51), paraplegic (T6-L4, AIS A, n=32), and able-bodied subjects (n=36). Values are shown in mean±standard deviation. Nocturnal dip was calculated as (systolic blood pressure [SBP] nighttime – SBP daytime)/SBP daytime x 10042 from values of sensorimotor complete (AIS A) SCI and able-bodied subjects of studies presented in Table 1. Significant differences in nocturnal SBP dip were found between tetraplegic and paraplegic subjects (p=0.02), and tetraplegic and able-bodied subjects (p=0.03; Mann-Whitney U test).