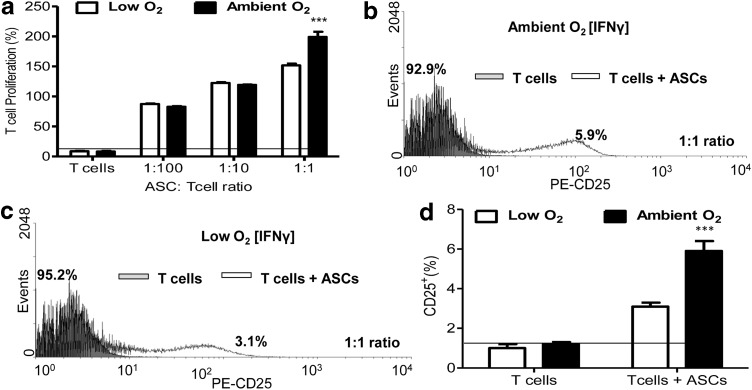
FIG. 2.
Naive T-cell proliferation and activation following direct coculture with ASCs under low O2 and ambient O2 culture conditions. Naive CD4+ T cells were isolated from peripheral blood of breast cancer patients. ASCs were treated with IFN-γ for 5 days, and then treated with 50 μg/mL mitomycin c to inhibit growth. Naive CD4+ T cells were cocultured with IFN-γ-treated ASCs at cell concentrations of 1:100 (1,000 ASCs:100,000 T cells), 1:10 (10,000 ASCs:100,000 T cells), and 1:1 (100,000 ASCs:100,000 T cells) for 3 days. T-cell proliferation was quantified through bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation. CD4+ T-cell proliferation (%)=(ETcell+ASC/ETcell)×100, where ETcell+ASC=proliferation absorbance measurement for naive T-cell+ ASC group, and ETcell=proliferation absorbance measurement for T-cell group. (a) Percent (%) T-cell proliferation following coculture at varying ratios. Percent (%) CD25+ T cells were evaluated following 1:1 coculture with ASCs by flow cytometry under (b) ambient and (c) low O2 conditions. (d) Quantification of flow cytometric analyses in panels b and c for CD25 expression of T cells following coculture of ASCs with naive T cells. Three independent sets of experiments were performed for each treatment. Data are reported as mean (μ)±SE. Significance: ***P<0.001.