Figure 1. Pre- and post-treatment of PKC inhibitors protect primary cultured hepatocytes from APAP.
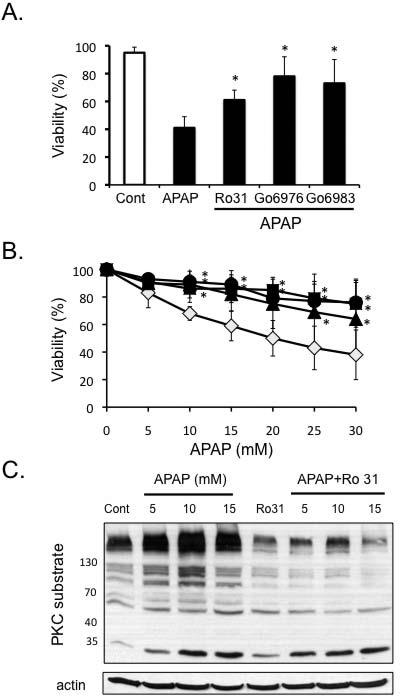
A) Pre-treatment of PKC inhibitors protects against APAP cytotoxicity. Hepatocytes were pre-treated 1 h with PKC inhibitors prior to the addition of APAP (5 mM). APAP was subsequently not removed and viability assessed at 18 hours. B) Post-treatment of hepatocytes with PKC inhibitors protects against APAP. Hepatocytes were treated with APAP for 2 h, then APAP was removed, and the cells were treated with different PKC inhibitors or DMSO for control [(broad-spectrum PKC inhibitors - Ro-31-8425 (5μM; ▲), Go6983 (10μM; ●) or classical PKC inhibitor - Go6976 (10μM; ■), or DMSO (control, ◇)]. Necrotic cells were determined using Sytox green 16-24 h after APAP treatment. Results are mean ± S.D. * p value ≤ 0.05 versus APAP treatment alone. C) APAP treatment of hepatocytes increases PKC activity (proteins phosphorylated by PKC), which is blocked by Ro-31-8425 treatment. Hepatocytes were treated with various doses of APAP with or without Ro-31-8425 (post-treatment). PKC activity was assessed in hepatocyte lysate by Western blot using an antibody that recognizes proteins phosphorylated by PKC (PKC recognition motif: serine residues surrounded by arginine or lysine at the – 2 and +2 positions and a hydrophobic residue at the +1 position).
