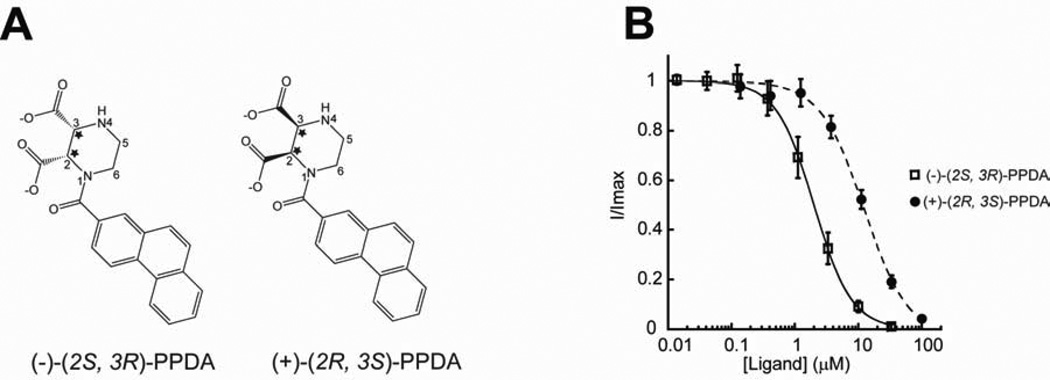
Figure 4. GluN1/GluN2A NMDA receptors selectively bind (−)-PPDA over (+)-PPDA.
(A) Enantiomers of PPDA showing two chiral centers (stars) at the 2 and 3 positions of the piperazine ring. PPDA used in this crystallographic study is the enantiomeric mixture available commercially (TOCRIS). However, the electron density indicates the exclusive presence of (−)-(2S, 3R)-PPDA as shown in Figure 3C. (B) Inhibition of glycine/l-glutamate ion channel current by (+)-(2S, 3R)-PPDA (filled circle) or (−)-(2S, 3R)-PPDA (square) in the GluN1-1a/GluN2A NMDA receptors. The currents are formed by coapplication of 100 µM of glycine and 5 µM of l-glutamate and inhibited by various concentrations of PPDA. All of the recordings are done using the TEVC method. Error bars represent s.d.