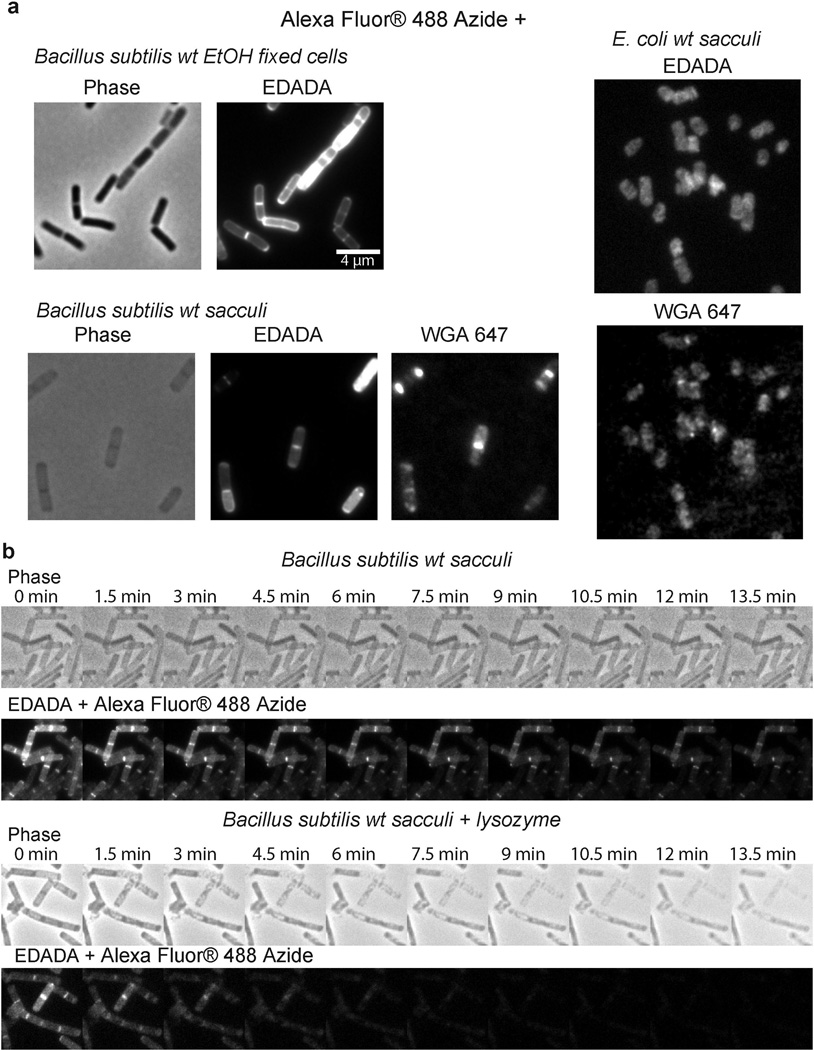
Extended Data Figure 4. EDA-DA labeling is specific to the PG of bacteria.
a, Alexa Fluor 488 Azide ‘clicked’ sacculi from B. subtilis and E. coli cells grown with 0.5 mM EDA-DA for several generations retained the alkyne label. The labeled cells were clicked before sacculi purification in the case of B. subtilis and after purification in the case of E. coli. Experiment was conducted in biological duplicates and images are representative of five fields viewed per replicate. b, The EDA-DA signal retained on the isolated PG can be released by PG-digesting enzymes (~ 10 mg/mL lysozyme + 200 µg/mL mutanolysin). The kinetics of signal disappearance from the lysozyme treated sacculi is much faster than the kinetics of the photo-bleaching during the time-course, indicating that the loss of signal is due to hydrolytic activity of lysozyme. Three experimental replicates were performed.