Figure 5.
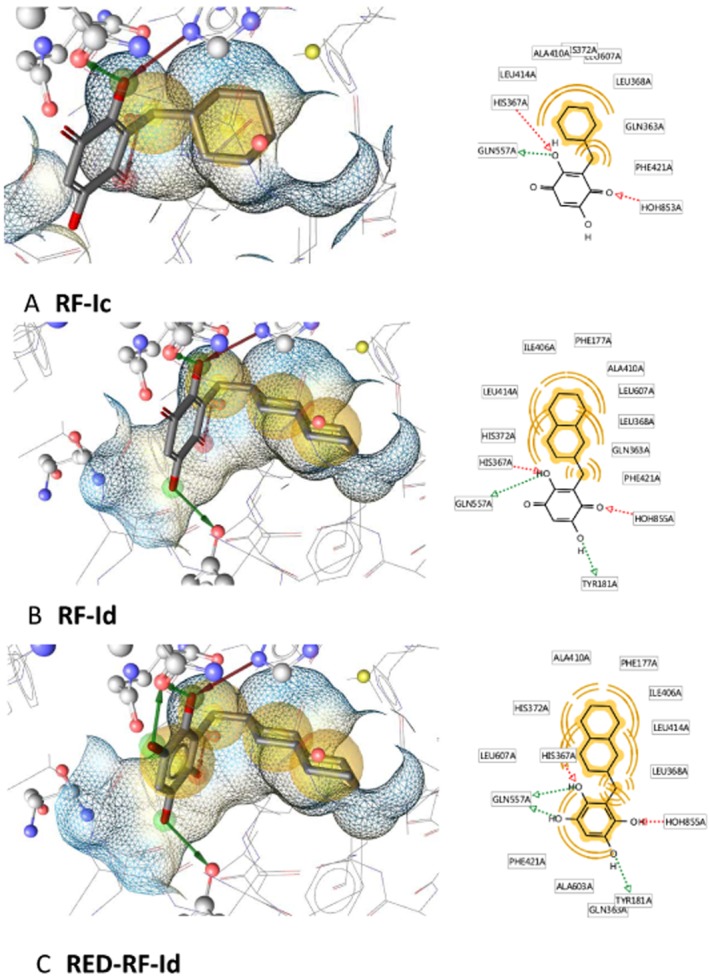
Docking poses for RF-Ic, RF-Id and RED-RF-Id. The wireframe represents the surface of the binding pocket. The yellow spheres indicate hydrophobic parts of the molecule and the arrows mark hydrogen bond donors (green) and acceptors (red). (A) Docking pose of inactive RF-Ic. The quinone part of the molecule forms hydrogen bonds with His367, Gln557 and H2O853. However, the hydrophobic channel of 5-LOX is only incompletely filled by the ligand. (B) Docking pose of active RF-Id within the binding pocket. Interactions with Gln557, Tyr181, His367 and H2O855 are shown. The hydrophobic part of the molecule effectively fills the substrate channel. (C) RED-RF-Id within the binding pocket forms more bidirectional hydrogen bonds than in the oxidized quinone form (RF-Id, see B). Interactions with Gln557, Tyr181, His367 and H2O855 are shown.
