Figure 3.
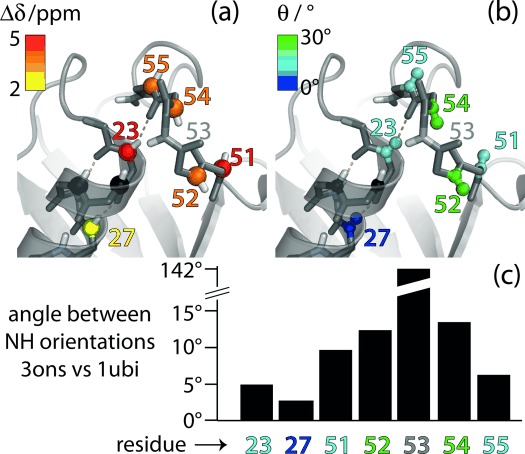
Residues involved in the conformational exchange process in ubiquitin. a) Residue-wise chemical-shift differences Δδ (obtained from data in Figure 2 a) and b) jump angles θ (obtained from Figure 2 b) are plotted onto the structure of ubiquitin crystals used in this study (PDB 3ons). Amides 24 and 25 (black spheres) are invisible in NH correlation spectra, presumably due to exchange broadening.[11] c) Residue-wise differences of the N–H orientations in the crystal structure used here (type-II β-turn) and in a structure featuring a type-I β-turn (PDB 1ubi). These angles were obtained by aligning the two structures to all secondary structure elements and extracting the direction of the respective N–H bonds.
