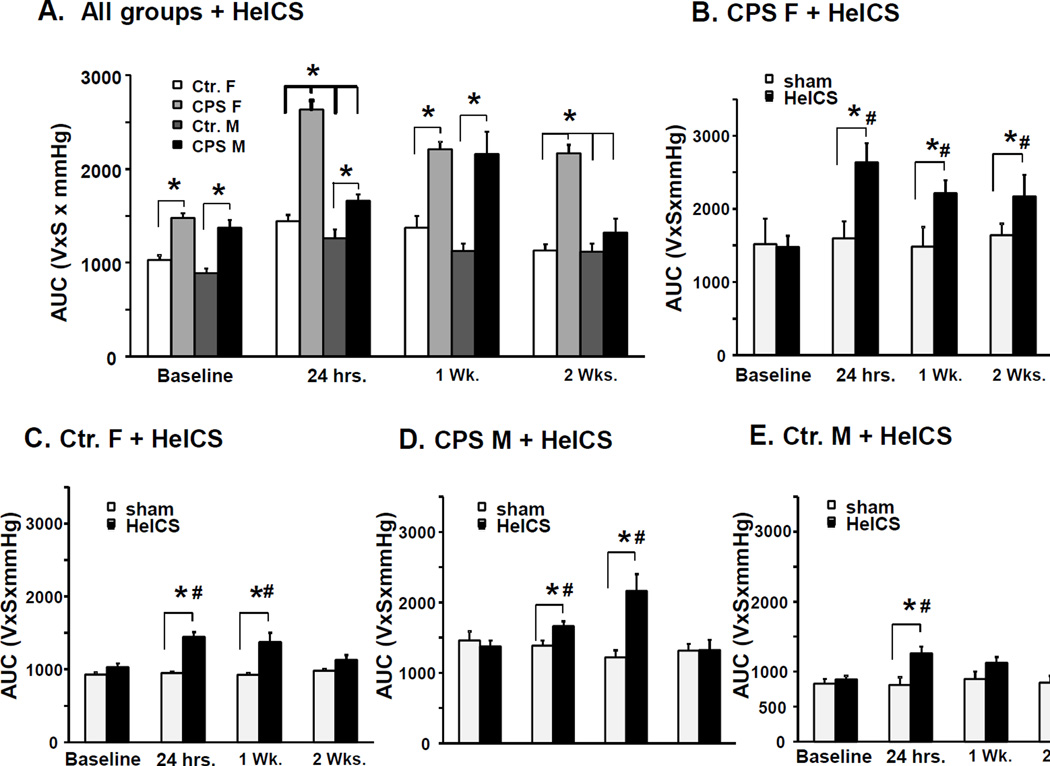
Figure 1.
Effects of CPS followed by adult chronic stress on colon sensitivity to CRD in male and female rats. A. Bar graphs display area under the curve of EMG to graded CRD of male and female CPS and control rats before stress at 24 hours, 1 week and 2 weeks after the end of adult 2× HeICS, *p<0.05 vs. baseline. Baseline measurements were obtained from female Ctr (n=12), female CPS (n=12), male Ctr (n=20) and male CPS (n=10) rats. Ctr. (n=8), female CPS (n=8), male Ctr (n=13) and male CPS (n=6) rats were subjected to the nine day 2× HeICS protocol, the remaining rats were sham stressed. B. Bar graphs display the average response to CRD of female CPS rats before and 24 hours, 1 week and 2 weeks after adult 2× HeICS compared to sham stressed female CPS rats. We observed a significant main effect of the interaction of stress×time (F3, 30=4.4, p=0.01). Sensitivity to CRD in stressed CPS female rats was significantly greater than the pre-stress baseline and the sham stressed CPS female rats at 24 hours (p<0.001 and p=0.01, respectively), 1 week (p=0.001and p=0.02, respectively) and two weeks (p=0.002 and p=0.04, respectively). C. Bar graphs display the average response to CRD of female control rats before (baseline) and 24 hours, 1 week and 2 weeks after adult HeICS compared to sham stressed female control (Ctr.) rats. There was a significant main effect of stress (F3, 30=21.2, p<0.001), but not of time (F3, 30=2.12, p=0.12) or interaction between stress and time (F3, 30=2.42, p=0.085). Sensitivities to CRD were significantly greater in stressed rats compared to pre-stress baseline at 24 hours (p<0.001) and one week (p<0.001) but not at 2 weeks (p=0.24), and to sham stressed females at 24 hours (p=0.014) and 1 week (p<0.001) but not at 2 weeks (p=0.95). D. Bar graphs display the average response to CRD of male CPS rats before (baseline) and 24 hours, 1 week and 2 weeks after adult HeICS compared to sham stressed male CPS rats. There was a significant main effect of the interaction of stress×time (F3, 30=7.88, p<0.001). Sensitivity to CRD was significantly greater than pre-stress baseline at 24 hours (p=0.001) and 1 week (p=0.018), and greater than sham stressed male rats at 24 hours (p<0.001). E. Bar graphs display the average response to CRD of male Ctr. rats before (baseline) and 24 hours, 1 week and 2 weeks after adult 2× HeICS compared to sham stressed male Ctr. rats. *p<0.05 vs. sham; # p< 0.05 vs. baseline.